oooo

o
oooo
oooo

BSL Version
o
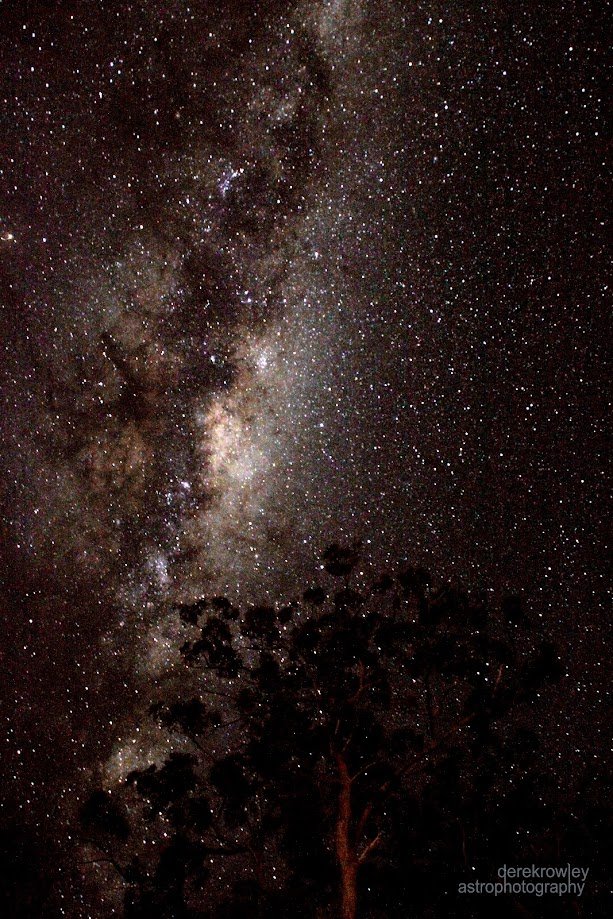
- Our milky way – this bright galaxy is a single astronomical object, even though it contains billions of individual stars and is constantly forming new clusters of stars.
o
o
oooo

- The universe consists of energy and matters irregularly distributed throughout the continuum of curving space-time, but most of the matter and energy is invisible to humans.
o - In the astronomical community, there are six currently accepted categories for the objects;
……….–…star
……….–…planet
……….–…moon
……….–…comet
……….–…asteroid
……….–…gas
o
o
oooo
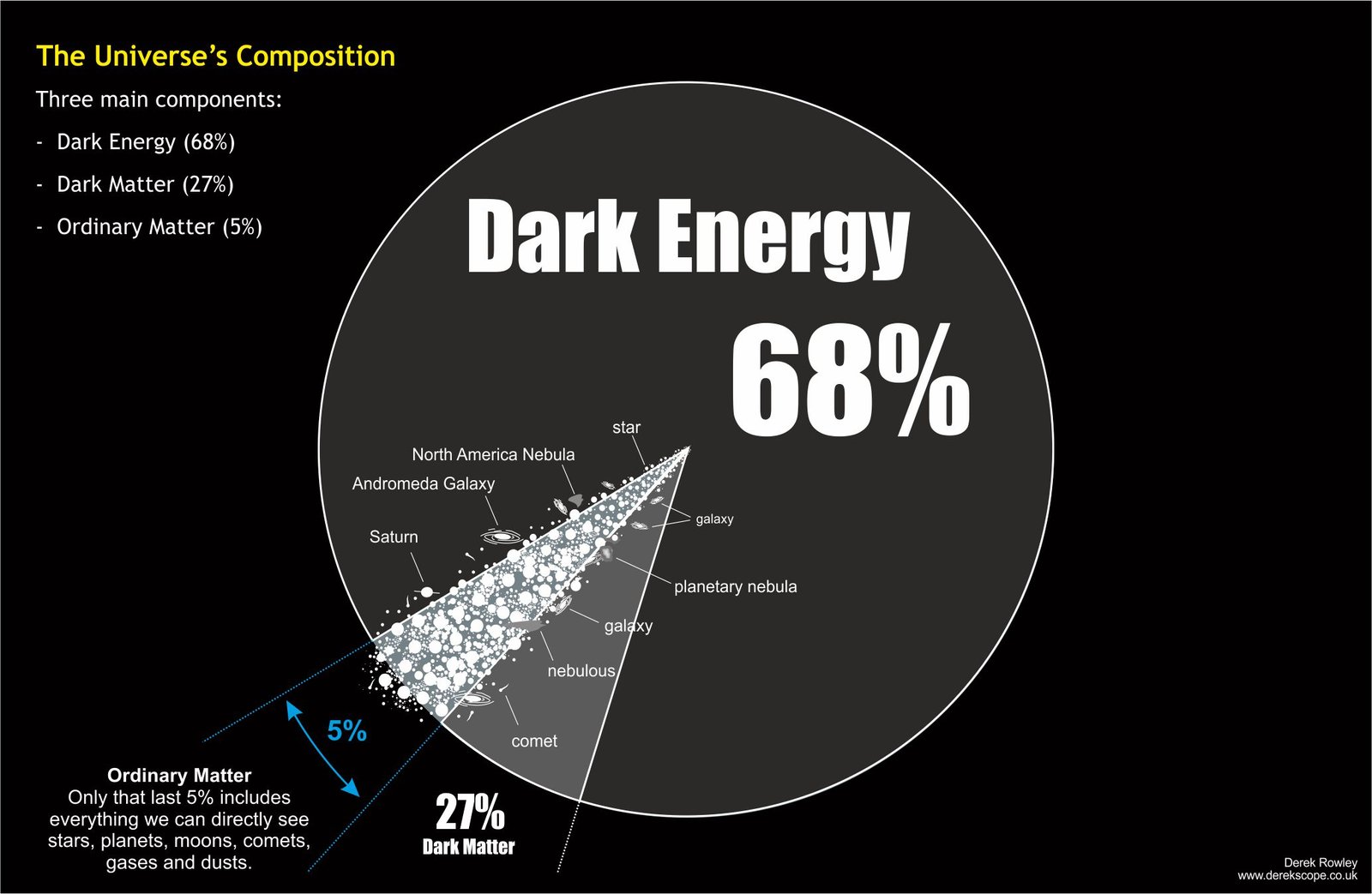
The Universe’s Composition
oooo
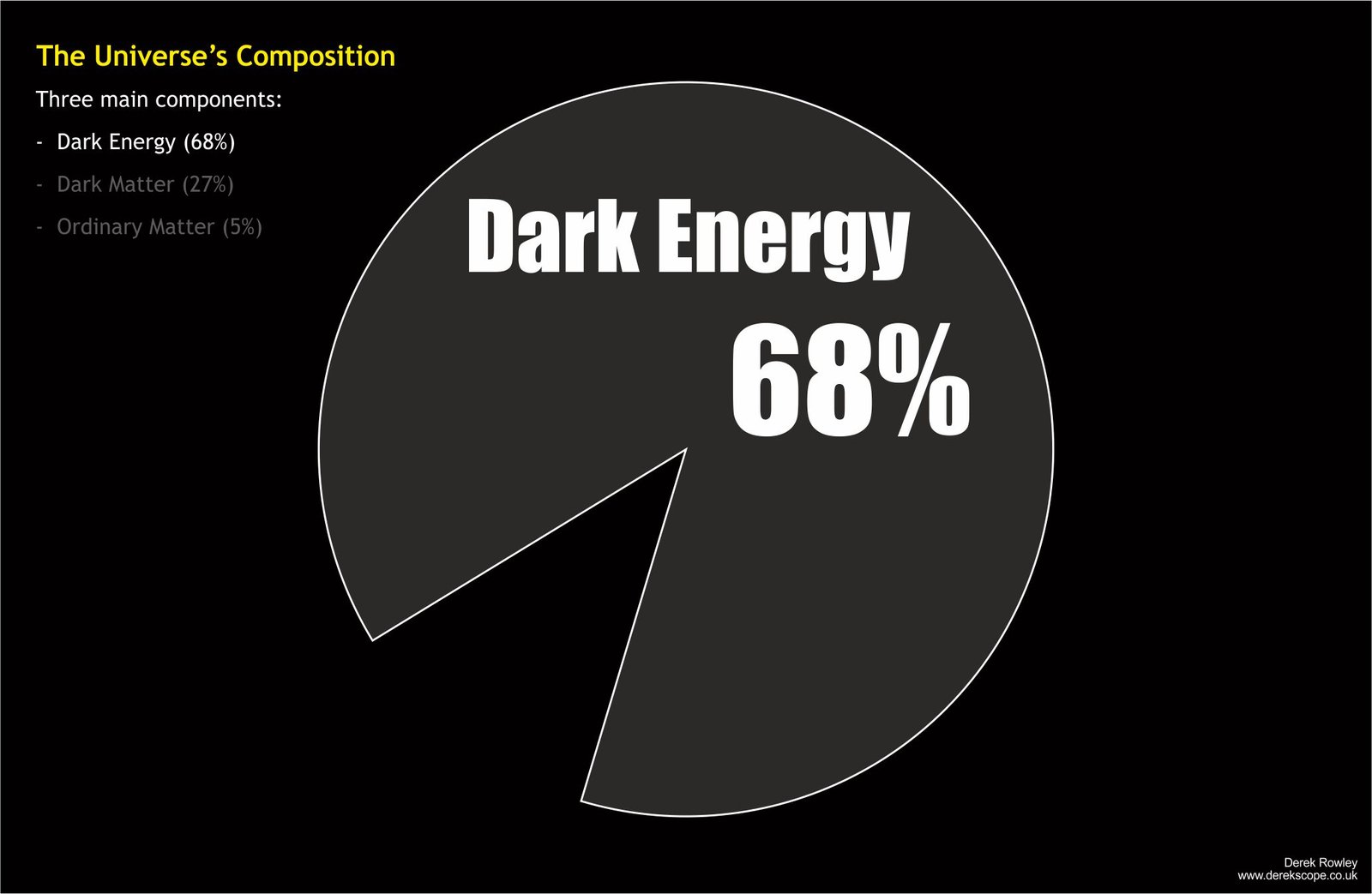
- Now scientists think that the Universe is made of 68% dark energy, 27% dark matter, and 5% ordinary matter in the form of stars and galaxies.
o - 5% Ordinary matter – this is clumped together in objects of varying sizes and densities.
The term ‘objects’ refers to individual items that astronomers can examine through telescopes.
o
o
o
The Universe’s behaviours
oooo
oooo
oooo
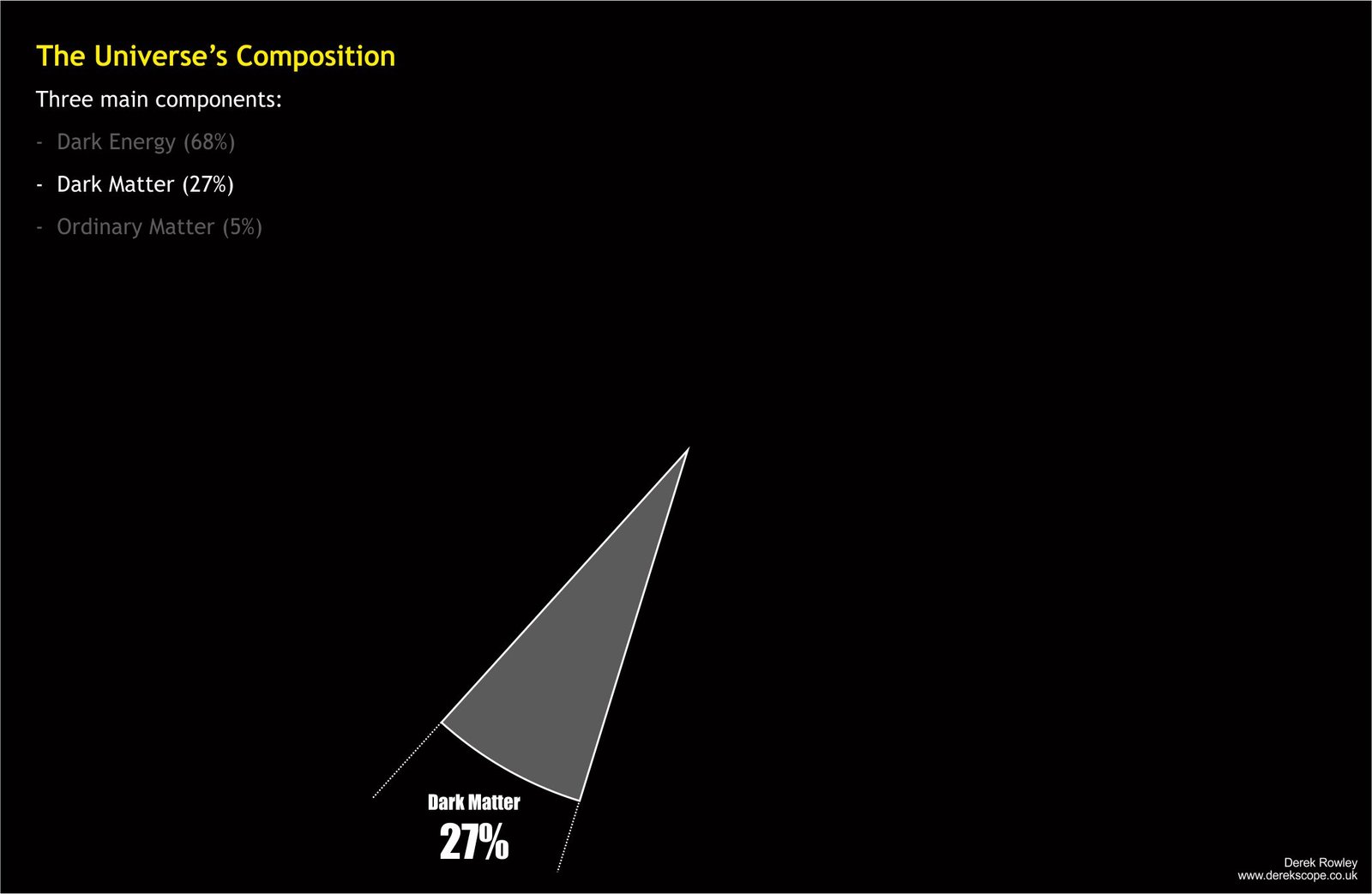
- Dark Matter (27%)
Dark – does not emit or absorb light.
Dark – does not collide.
Dark – does not heat up like gas.
Dark – providing the gravitational scaffolding for galaxies.
Dark – hold galaxies together.
Dark – control how fast galaxies rotate.
Dark – anchor galaxy clusters.
The Universe’s behaviours
oooo
- Dark Matter (27%)
Dark – does not emit or absorb light.
Dark – does not collide.
Dark – does not heat up like gas.
Dark – providing the gravitational scaffolding for galaxies.
Dark – hold galaxies together.
Dark – control how fast galaxies rotate.
Dark – anchor galaxy clusters.
The Universe’s behaviours
oooo
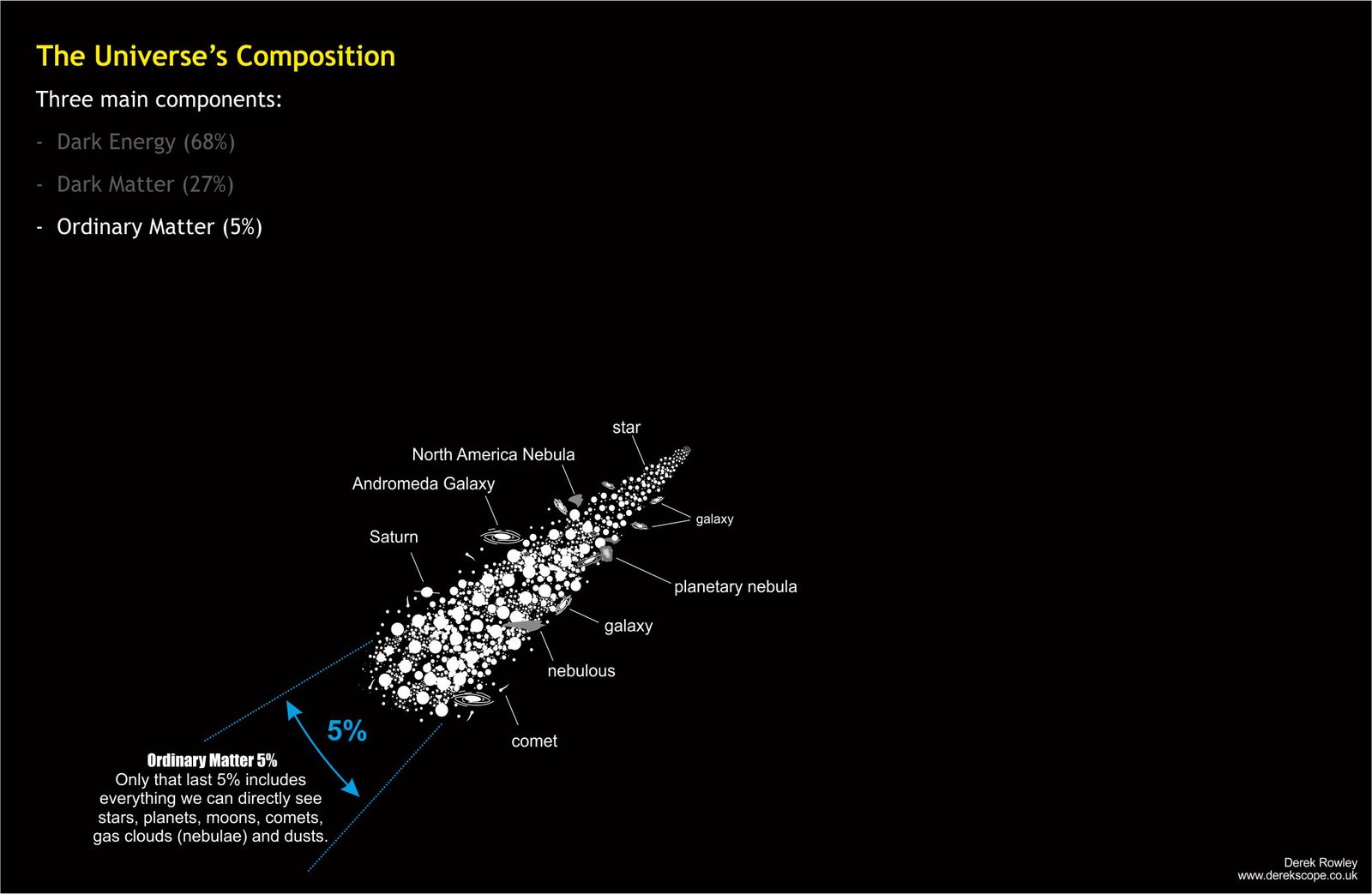
- Ordinary Matter (5%)
Ordinary – the stuff made of protons, neutrons and electrons.
Ordinary – responds strongly to gravity.
Ordinary – can cool, radiate energy and collapses under gravity into;
Ordinary ….stars, planets, nebulae, galaxies and galaxy clusters.
- This clumping is possible because Ordinary Matter (5%) can lose energy (through radiation), allowing it to cool and collapse – something dark matter cannot do.
o
o
oooo
On Earth matter exists in three forms as Solid, liquid and gas
o
o
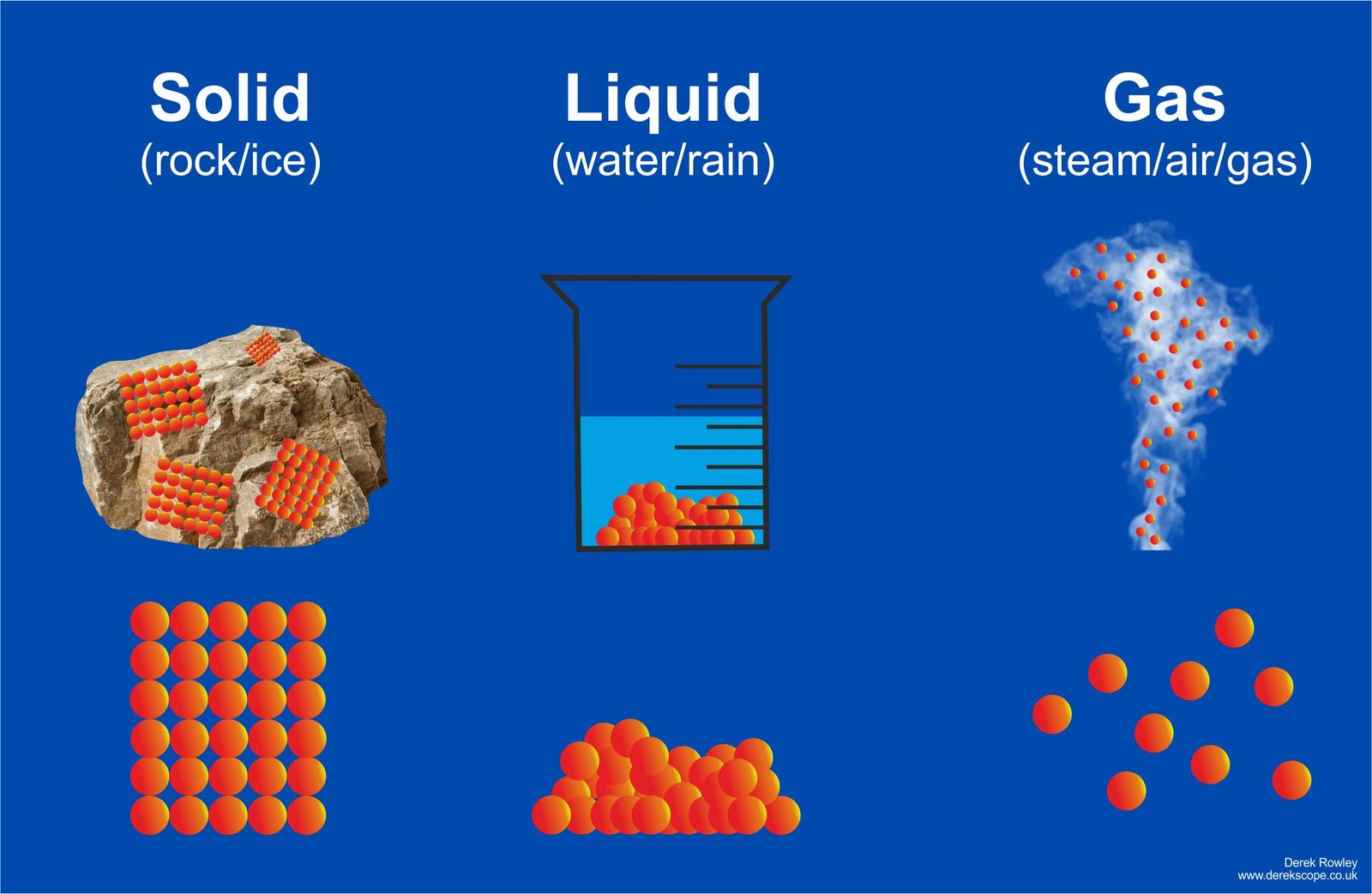
- The main different between solids, liquids, and gases is how their particles are arranged and move.
o
o
o
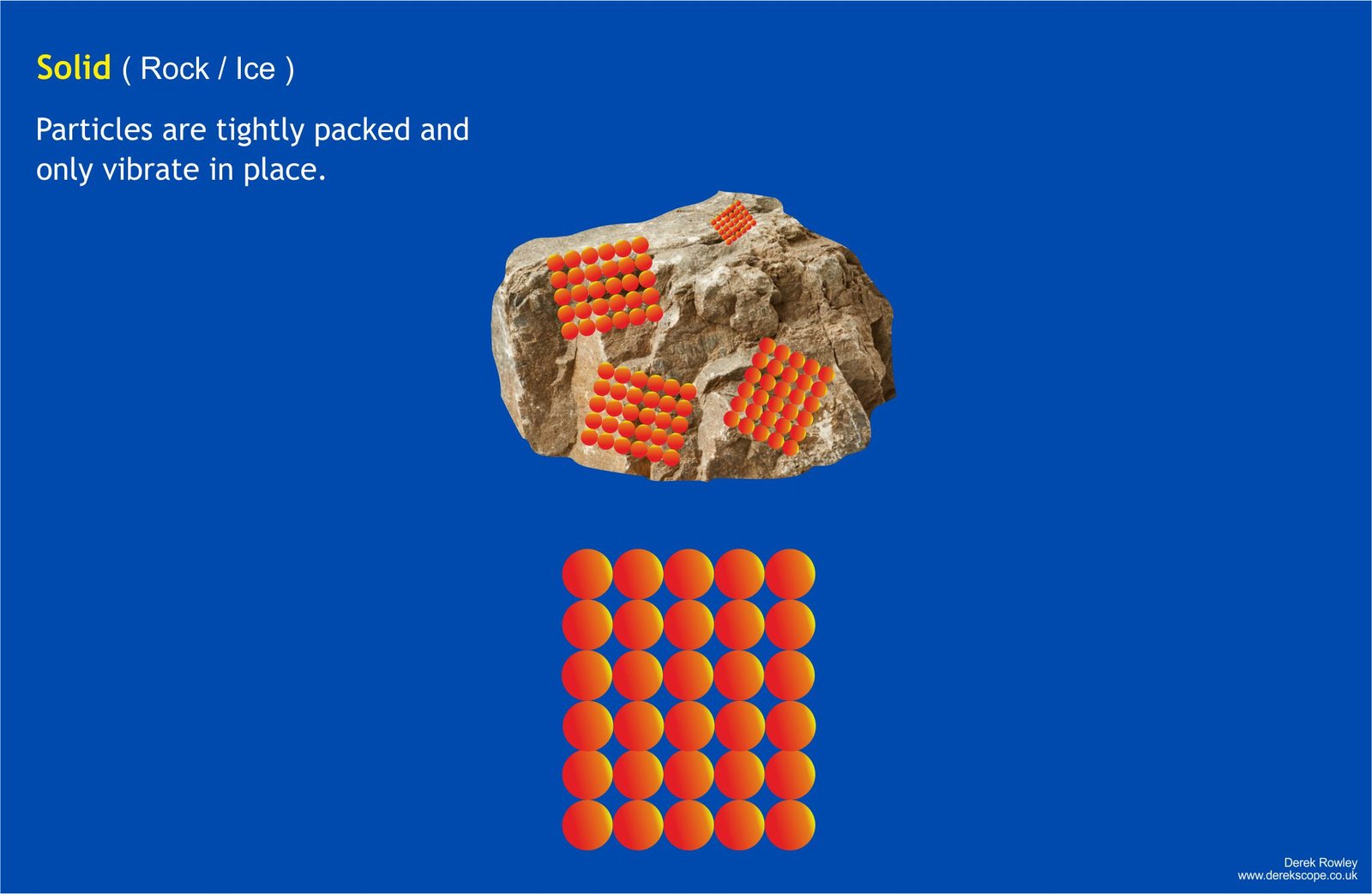
Solids ( Rock / Ice)
oooo
- Solids – Particles are close together and vibrate in fixed positions, giving solids a fixed shape. Solids can’t usually be compressed because there’s so little space between the particles.
o
o
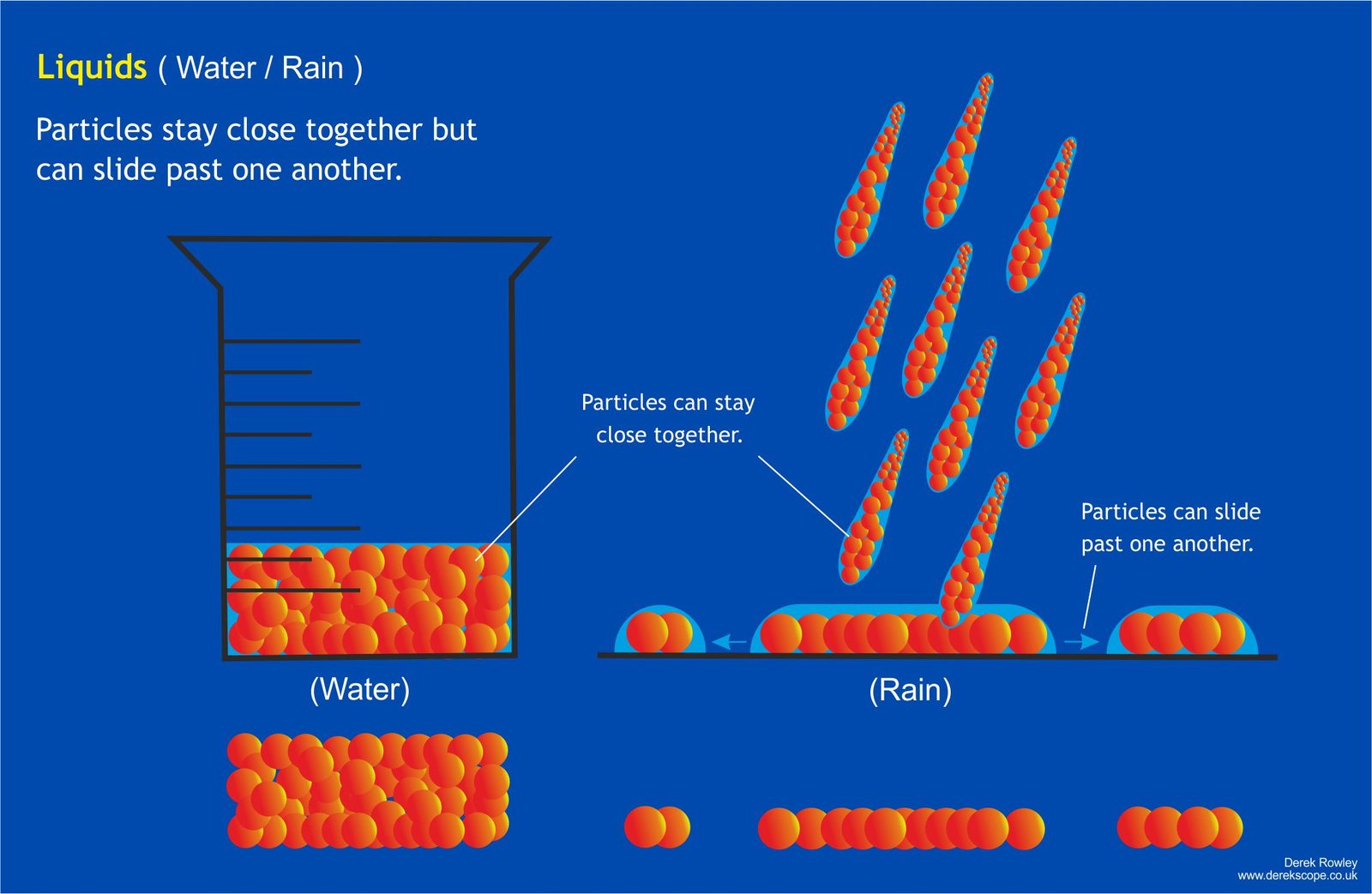
Liquids ( Water / Rain)
oooo
- Liquids – Particles are close together but randomly arranged, allowing them to move around and over each other. Liquids have a fixed volume but no fixed shape, so they flow and take the shape of their container.
o
o
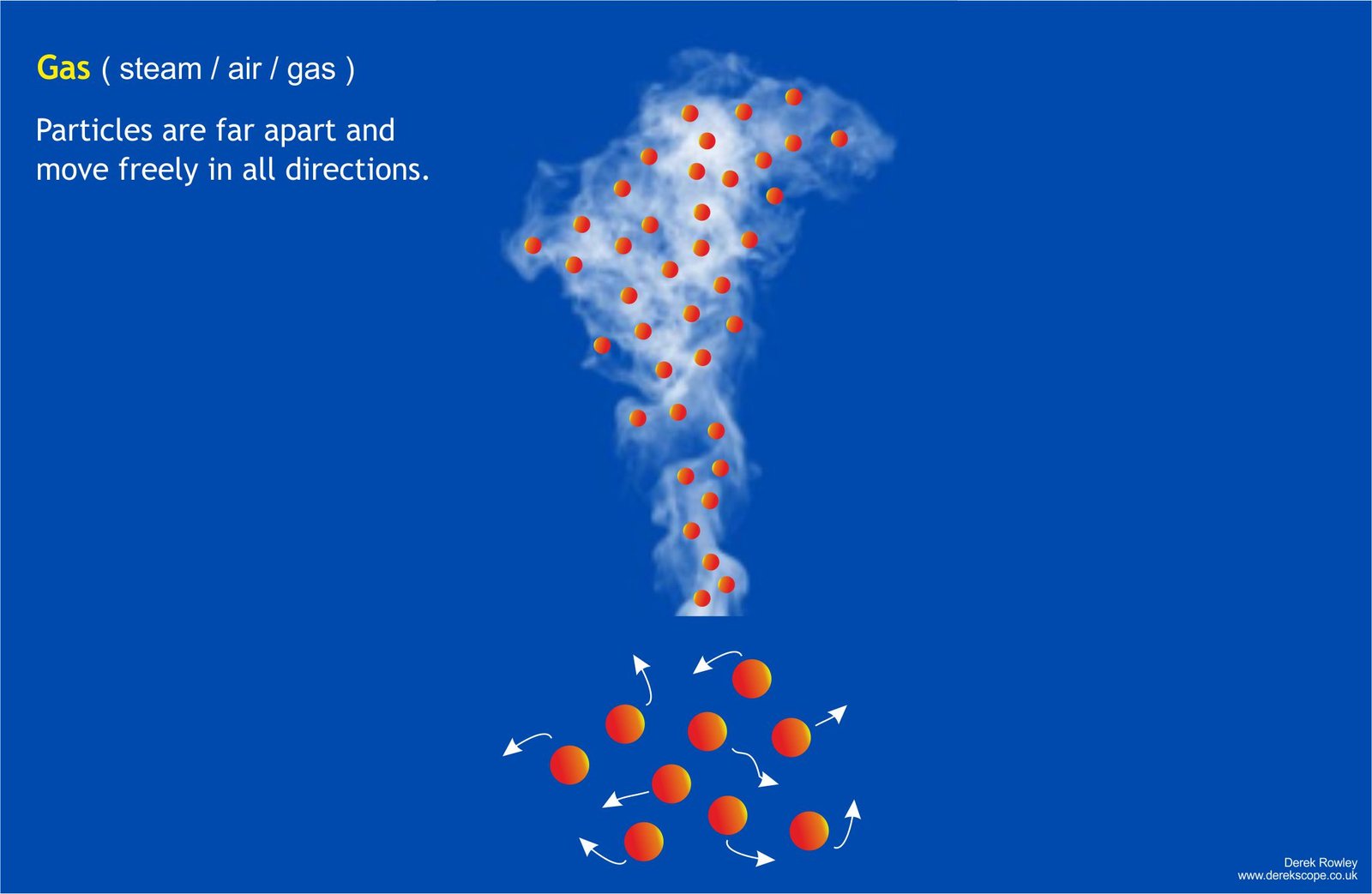
Gas ( steam / air / gas )
ooo
- Gases – Particles are widely spaced apart and move quickly in straight lines. Gases have no fixed shape or volume, so they expand to fill their container. Gases can be squeezed and compressed because there’s so much space between the particles.
o
o
The main difference between
solids, liquids, and gases
is how their particles are arranged and how they move.
o
- Solids
– ice/snow
– brick
– wood
– iron/copper
– car/train
– book/paper
– chair/table
– apple
- Liquids
– rain
– water
– petrol/oil
– vinegar
– paint
– juice
– tea
– milk
- Gases
– wind
– helium
– oxygen / air
– carbon dioxide
– hydrogen (gas)
– steam
– fog
– smoke
oooo
oooo
oooo
oooo
o
o
Objects in the Universe
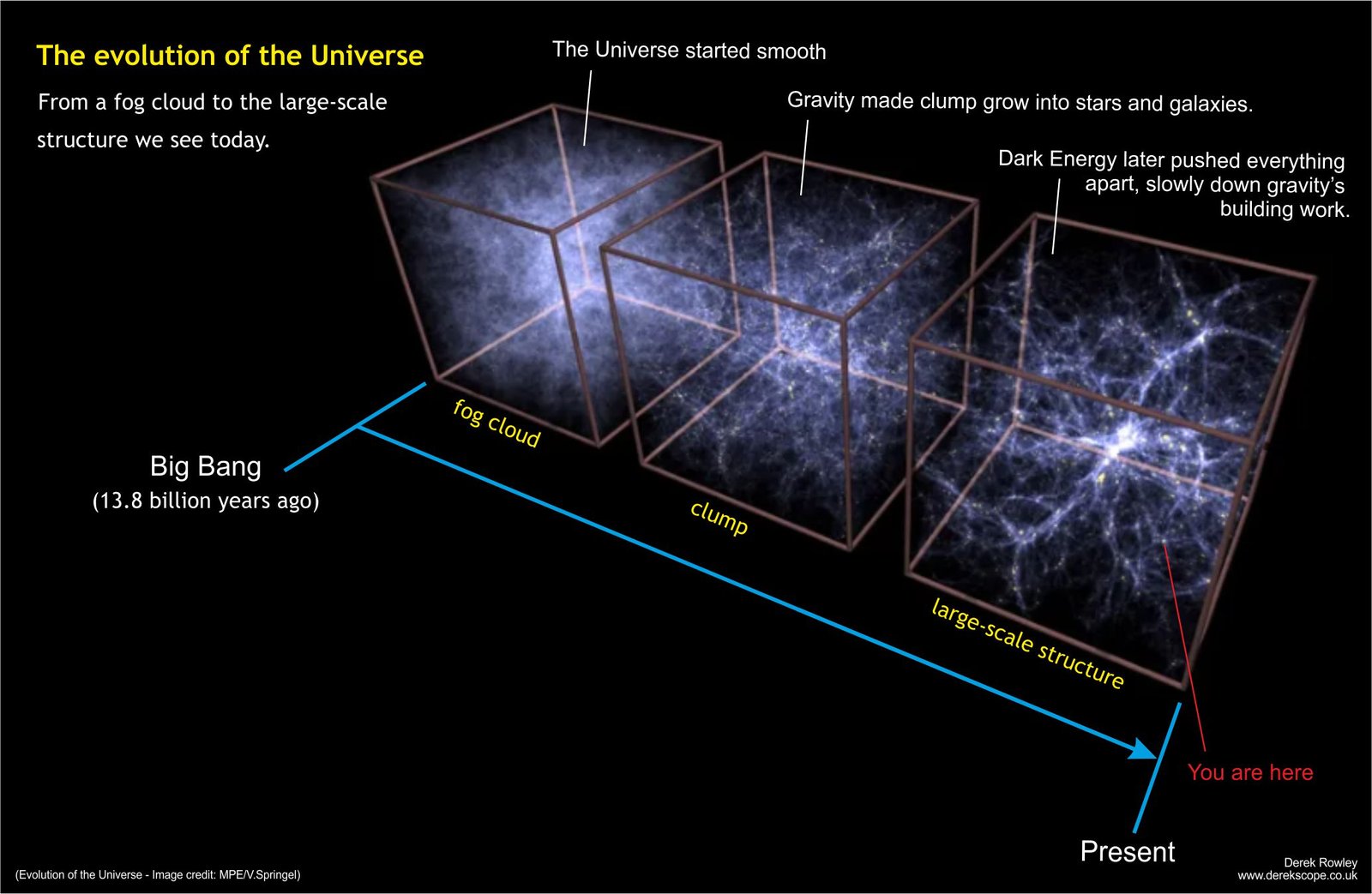
Matters and Energy irregularly
oooo
oooo
oooo
o
- Matters and Energy irregularly
The universe consists of matters and matters irregularly distributed throughout the continuum of curving space-time, but most of the matter and energy is invisible to humans.
o

BSL Version
o
o
oooo
Largest objects in the Universe

Group and Clusters of Galaxies
oooo
oooo
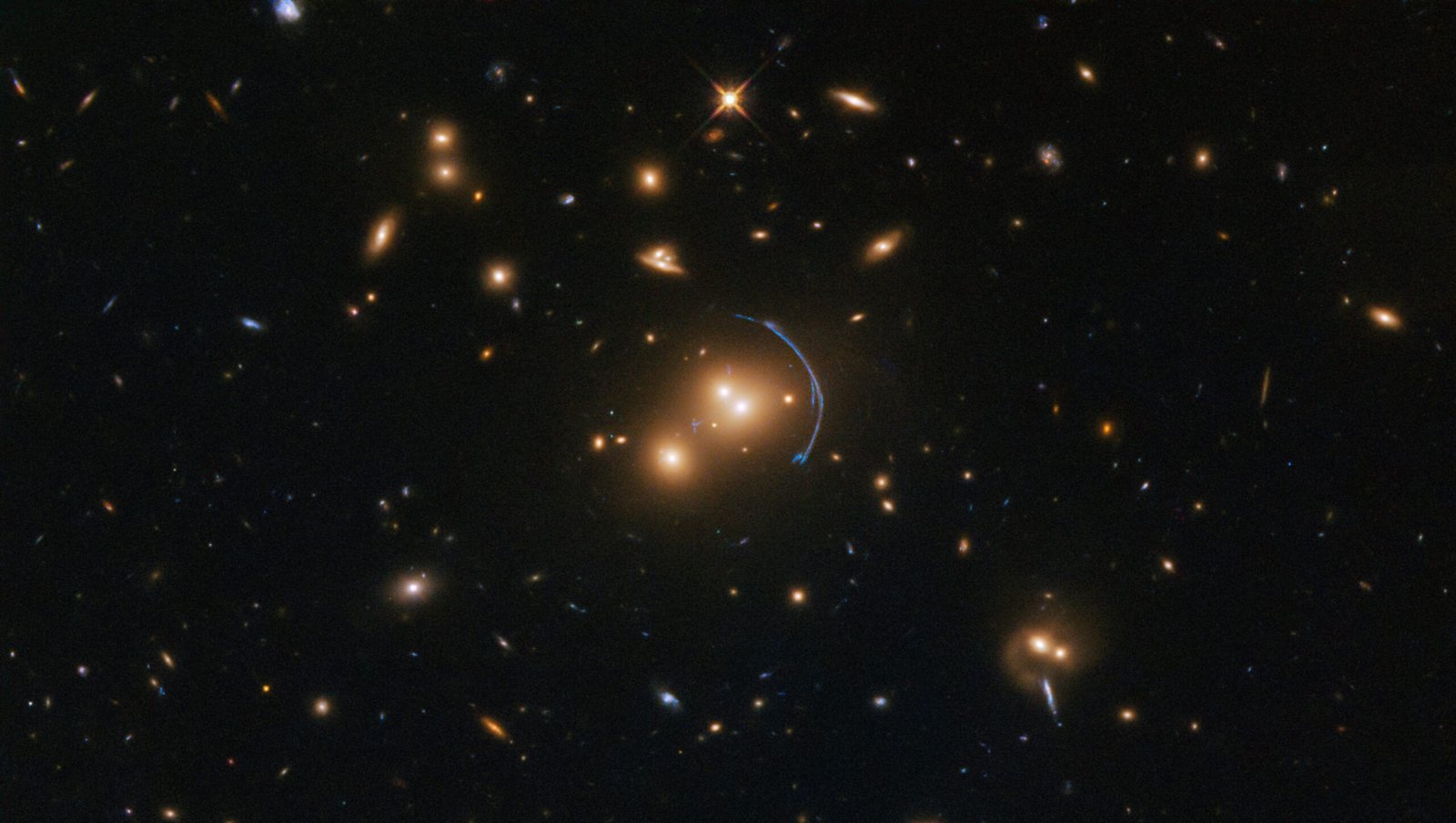
- Group and Clusters of Galaxies
The largest astronomical objects are galaxies, followed in terms of diminishing size by nebulas, stars, planets, moons, asteroids, comets and meteorites.
o
o - Although galaxies are made up of many billions of stars, they are considered to be a single objects – this because their stars orbit around a common centre of gravity and have the same relative motion with respect to the rest of the Universe.
o
o - Astronomical objects tend towards a spherical shape because the gravitational forces across the surfaces of a sphere are in equilibrium.
o
o
o - Rotation tends to distort spherical objects into a discus-shape – the Earth, for example bulges slightly around the Equator.
o
o - Objects of less than about 50 miles / 80km in diameter have insufficient mass to achieve a spherical shape, which is why the smaller asteroids all have irregular shapes.
o
o

BSL Version
o
o
oooo
oooo
oooo
Back to The Universe / next to Laws of Nature page.