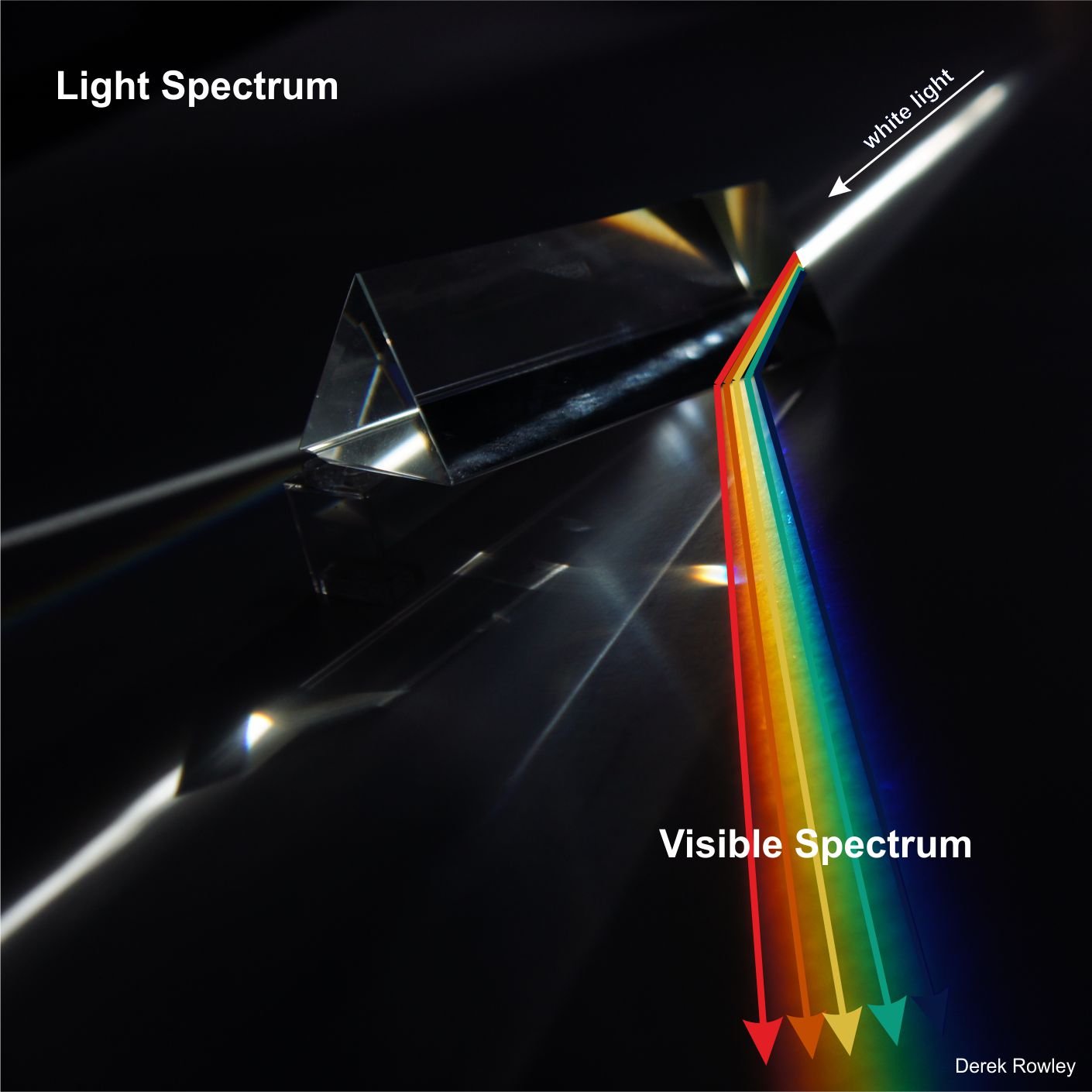

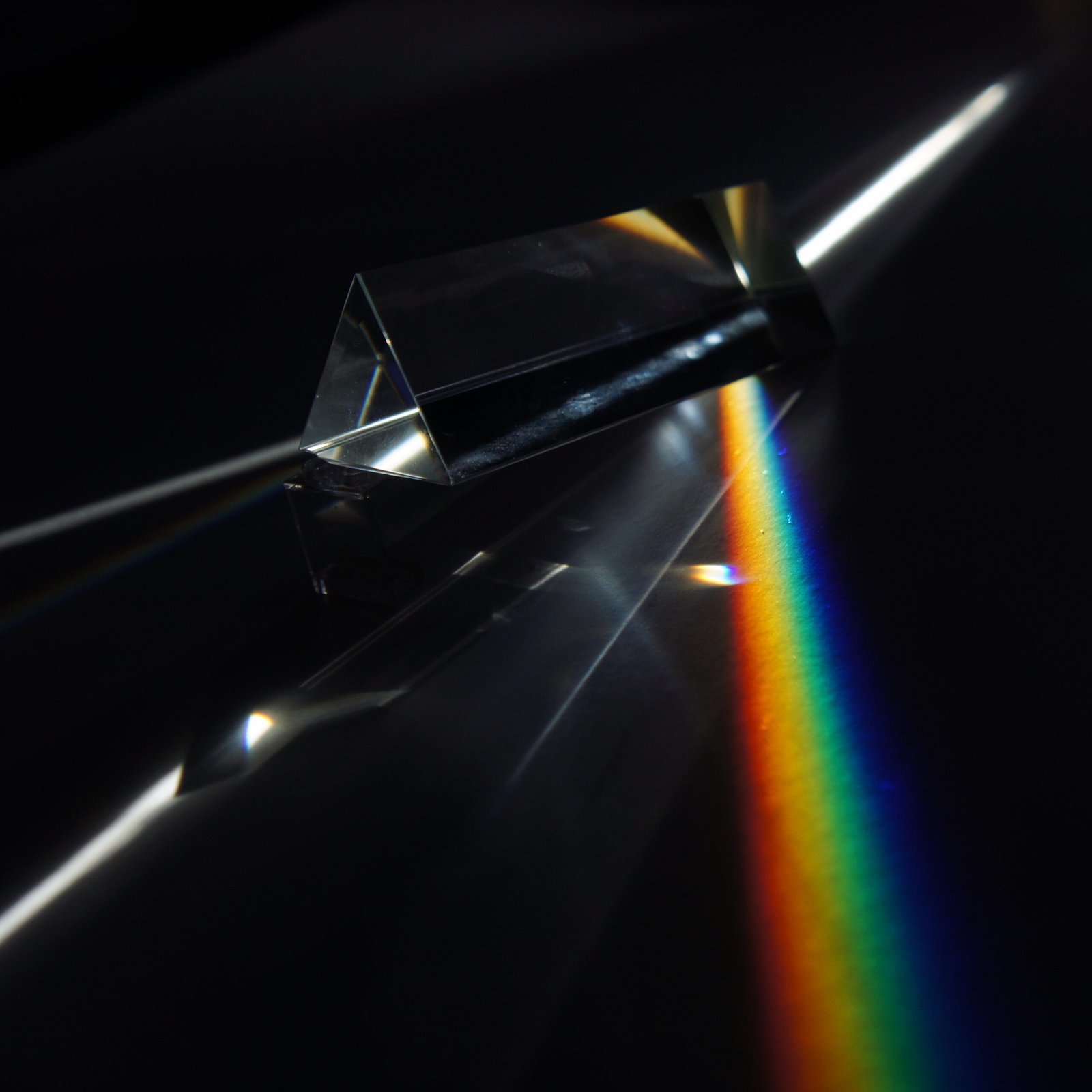
Spectrum
The distribution of colours produced when white light is
dispersed by a prism, changing in wavelength from
red (longest wavelength) to violet (shortest wavelength).
Seven colours are usually made out:
red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet.
oooo
oooo
oooo
- the fastest thing in the Universe is light – travels at 186,282 miles per second!
o - light rays always travel in straight lines.
o - the light passes from one material to another, light rays change direction – it’s called refraction.
o

oooo
oooo

BSL Version
oooo
oooo
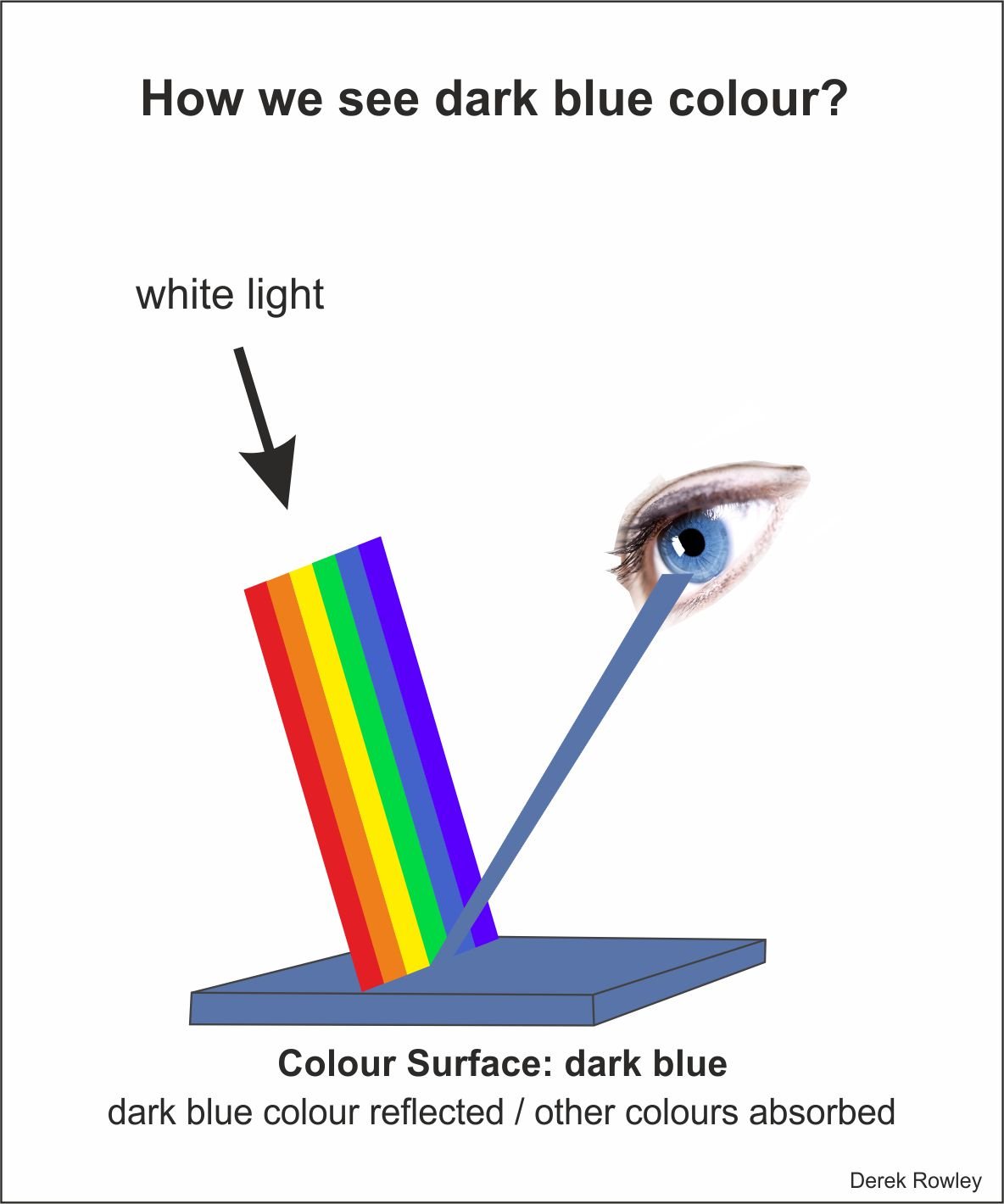
How we see the colours?
All colours are different wavelengths of light.





oooo

- the longest light waves that can be seen are red, and the shortest are violet.
o - light is a form of electromagnetic radiation – a light ray is a stream of tiny energy particles called photons.

BSL Version
- explaining about colour surfaces that we see.
oooo
oooo
Why can’t we see colours well in the dark?

oooo
oooo
oooo
oooo
oooo
- humans can’t see colour well at night because the cones in the eyes that are responsible for colour vision don’t work in dim light.
o - instead, the rods in the eyes, which are responsible for vision in dim light, take over.
o - rods are located on the outer edges of the retina and are much more sensitive to light than cones. However, rods don’t provide colour vision, so everything appears to be various shades of black and white and grey in dim light.
o

BSL Version
oooo
oooo
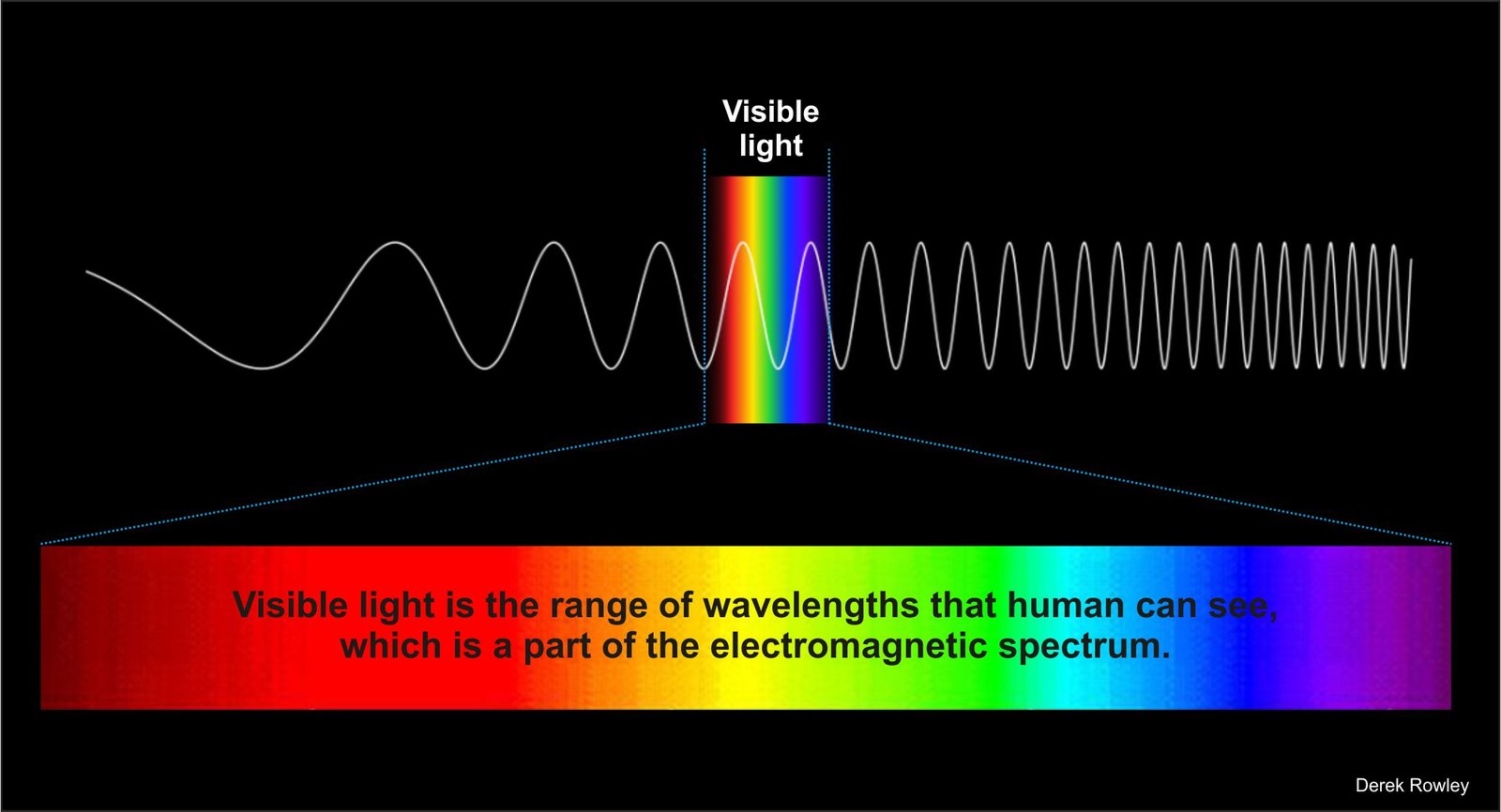
Electromagnetic Spectrum
oooo
oooo
oooo

- electromagnetic spectrum includes radio waves, ultraviolet light and X-Rays; visible light is the only part of the spectrum that can be seen by the human eye.
o - all light is given out by atoms – light can be viewed as small packets of energy (photons) -when hits an atom, energy is produced as light all light is given out by atoms.
o
o

BSL Version
oooo
oooo
Back to The Universe / next to Red Shift page.