Astronomical Unit (AU or au)
- a unit of length effectively equal to the average, or mean.
o - distance between Earth and the Sun, defined as 149,597,870.7 km or 92,955,807.3 miles. (nearly 93 million miles, so I do say 93 million miles.)
oooo

To measure the distance of a star
Astronomers use a baseline of 1 astronomical unit (AU),
which is the average distance between Earth and the sun.
oooo
o
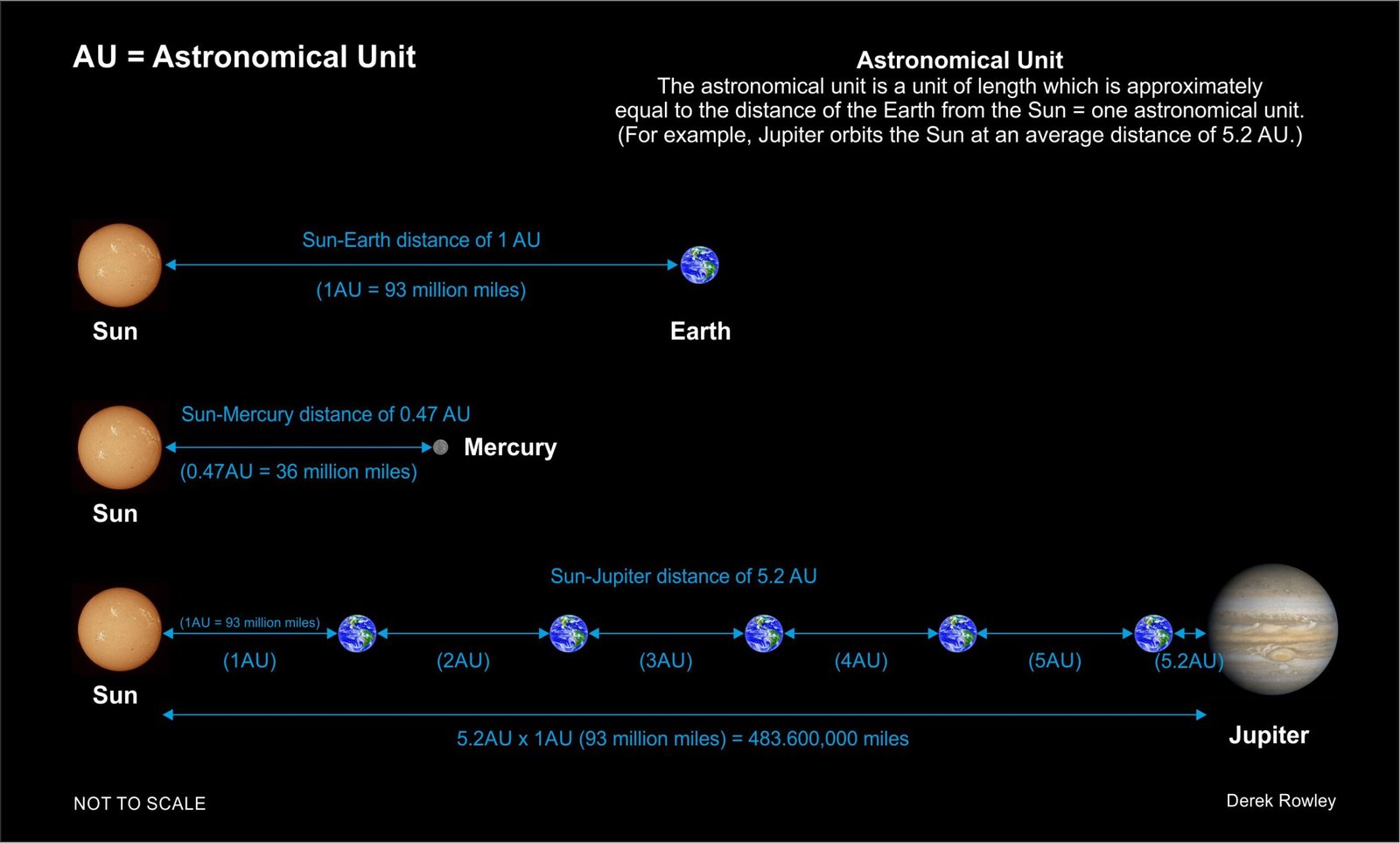
Example:
How far is Jupiter from the Sun?
The distance from the Sun to Jupiter is approximately 779 million km, or 484 million miles.
oooo
oooo
Explaining of distance in BSL
oooo
oooo
oooo
oooo

To measure the distance of a planet
o
Astronomers use a baseline of
1 astronomical unit (AU),
which is the average distance
between Earth and the sun.
o
oooo

oooo

BSL Version
BSL – Explaining of distance
- Sun >> Mercury
(distance of 0.47AU = 36 million miles)
o - Sun >>>> Earth
(distance of 1AU = 93 million miles)
o - Sun >>>>>>>>>>>> Jupiter
(distance of 5.27AU = 483,600,000 million miles)
OOOO
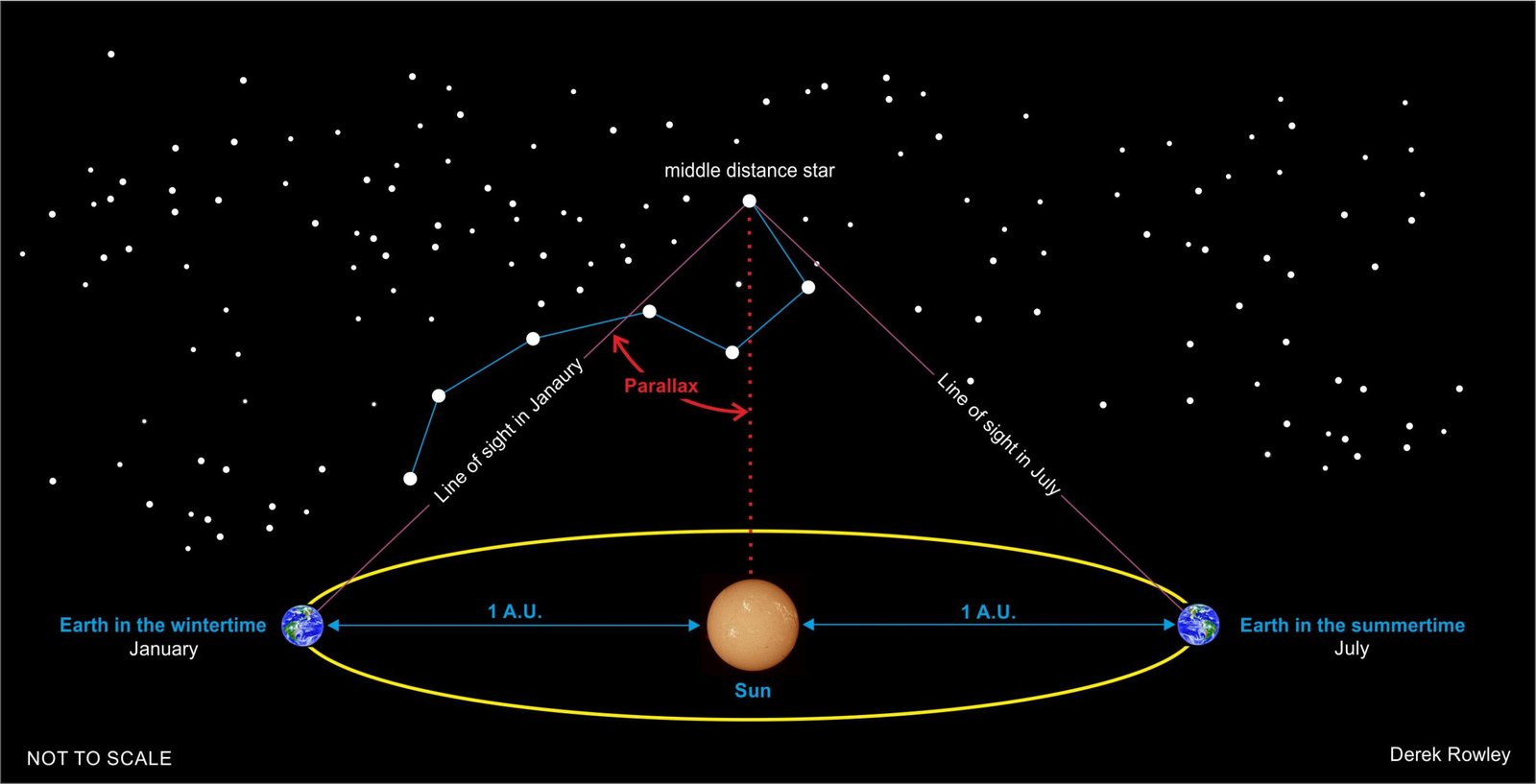
Parallax Shift
Parallax Shift
oooo
oooo
- nearby stars distance is calculated by measuring the slight shift in angle of each star in comparison to stars far away, as the Earth orbits the Sun; this is called “Parallax Shift”.
o - parallax shift, it can only be used to measure nearby stars, so astronomers work out the distance to faraway stars and galaxies by comparing how bright they look with how bright they actually are.

BSL Version
- explaining about parallax shift
oooo
oooo
Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram
oooo

oooo
oooo
oooo
- beyond classification and evolution, the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram offers invaluable insights into the fundamental properties and characteristics of stars.
o - each star’s position on the diagram reveals crucial information about its;
o
– luminosity
– surface temperature
– radius
– mass
o - these classes have particular colours. Spectral type is most often written across the top of the H-R diagram going from hot, blue “O” stars (very hottest, brightest stars) on the left to cool, more red “M” stars (very coolest, dimmest stars) on the right.
o - the seven spectral classes in order of surface temperature from hottest to coolest are;
o
o
O B A F G K M

BSL Version
- explaining about the hottest and coolest stars.
oooo
oooo
oooo
Back to The Universe / next to Light Spectrum page.