
oooo
Nuclear Power
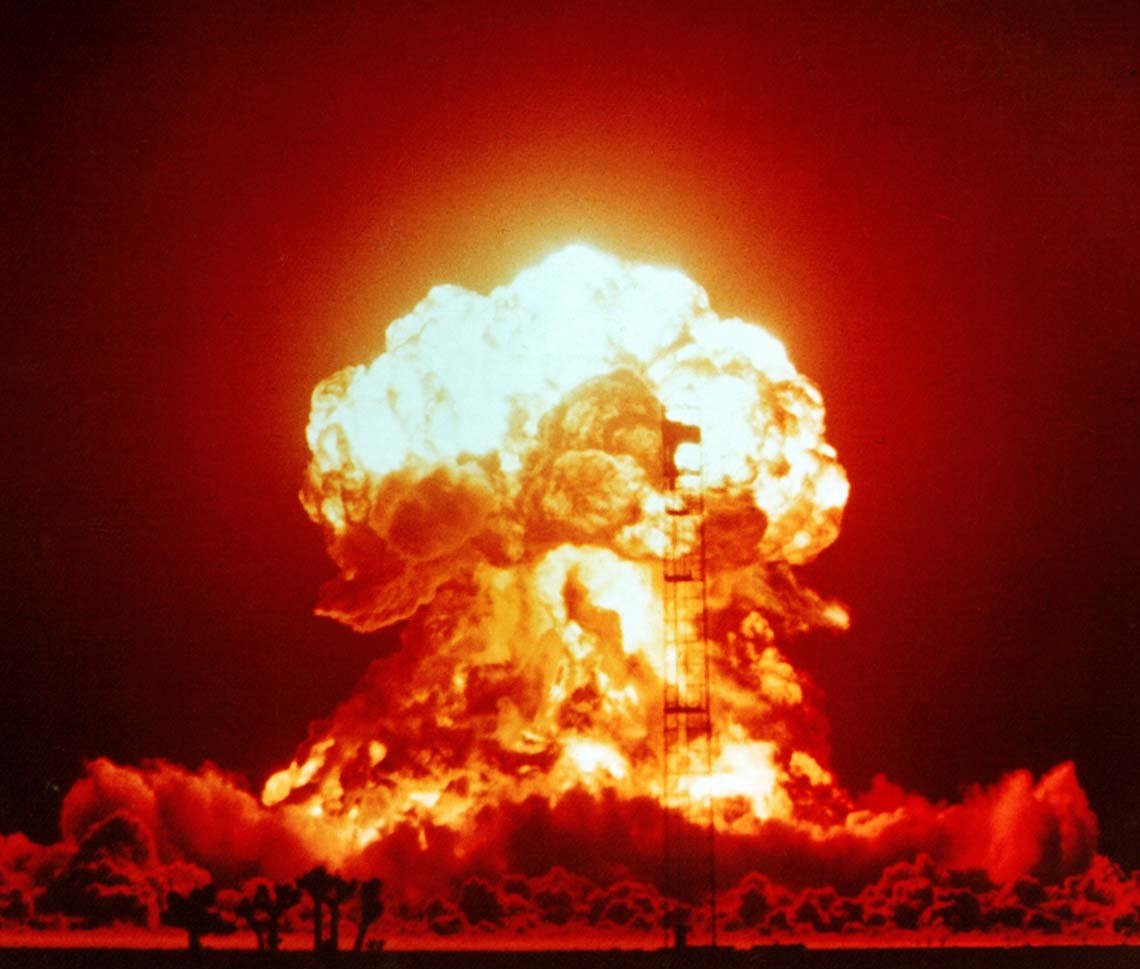
The extraordinary power locked in the nucleus of atoms
is shown when the explosion of a nuclear bomb releases some of the energy.
(See in BSL ![]() )
)
o
o
oooo
oooo
oooo
oooo
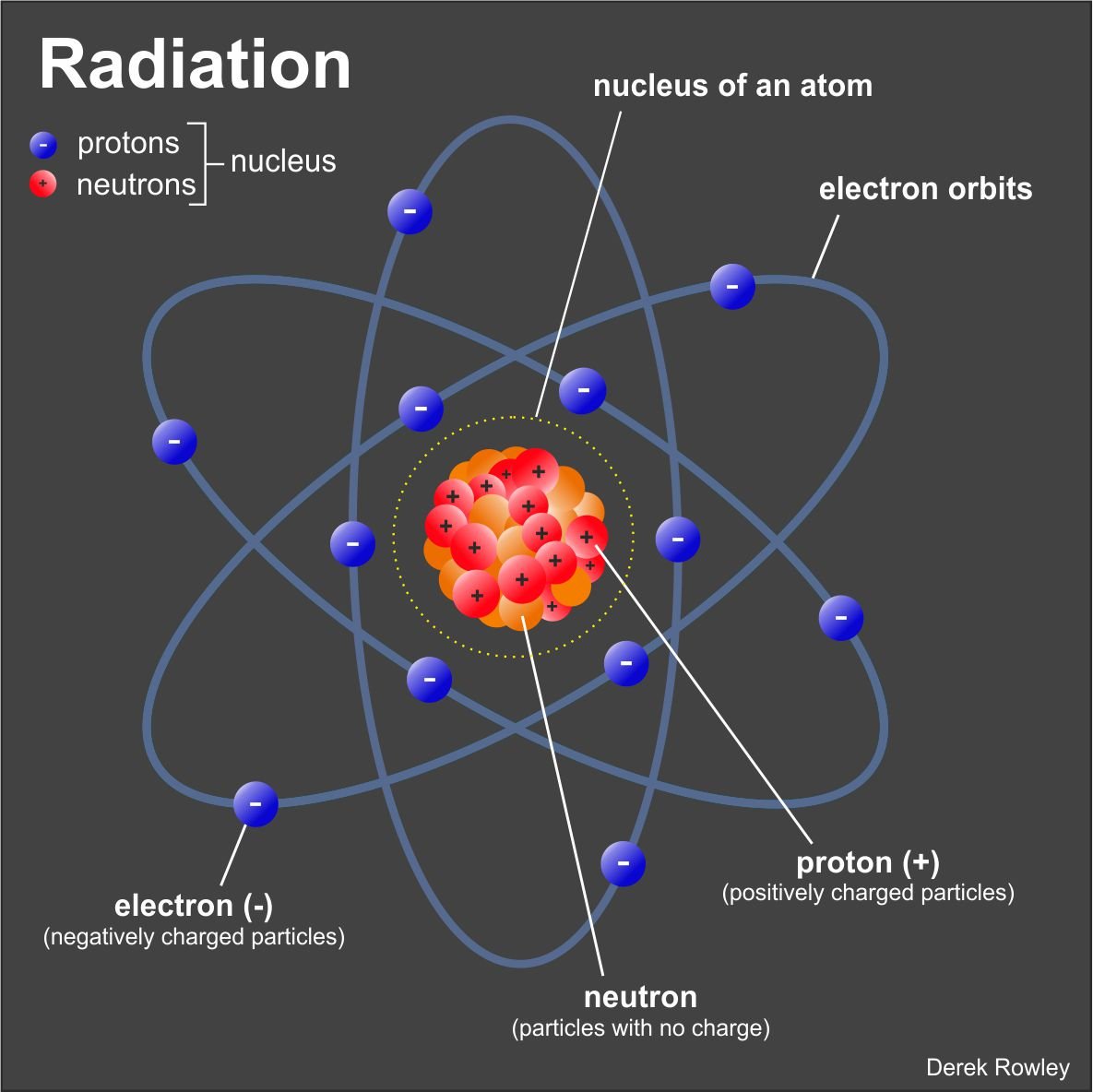
Atoms
The atom comprises three particles:
electrons (-), protons (+) and neutrons.
o
- energy that is given out by atoms at high speed is called radiation – two main forms; electromagnetic radiation and atomic particles.
o
oooo

BSL Version
oooo
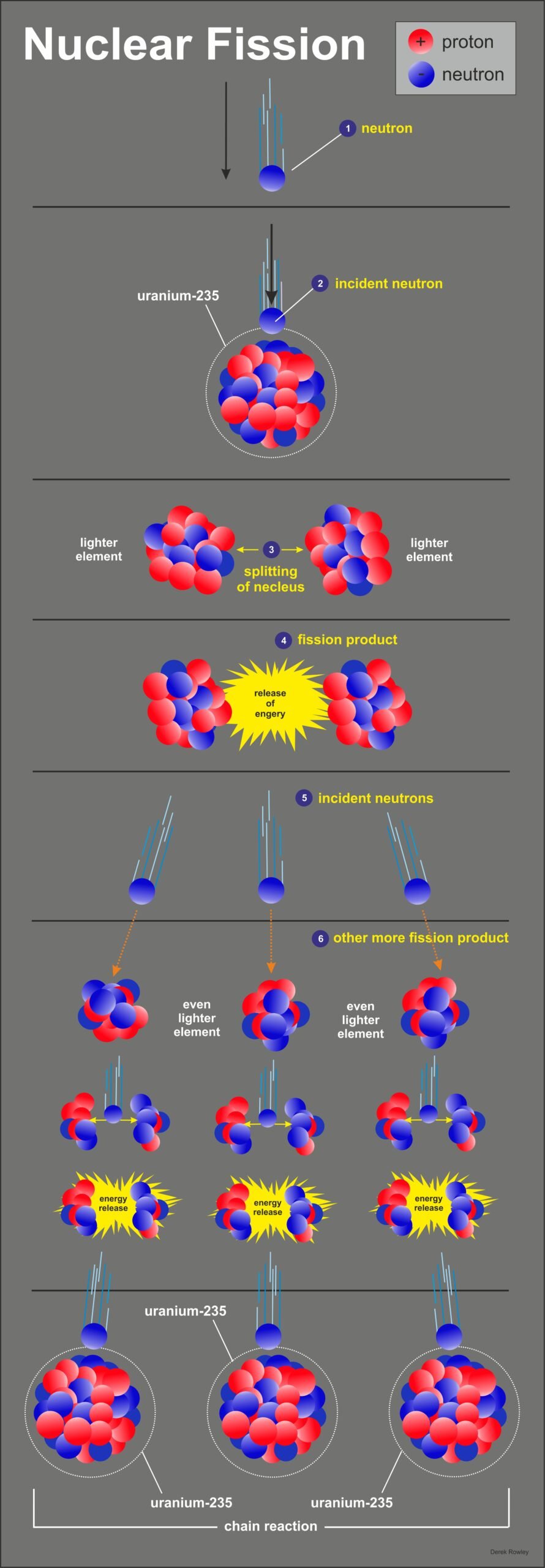
How does a nuclear fission work?
oooo
oooo

BSL Version
oooo
![]() neutron – strikes the nucleus and is absorbed.
neutron – strikes the nucleus and is absorbed.
![]() incident neutron – the nucleus absorbed causes the nucleus to undergo deformation. In around 10-14 seconds, one of the deformations is so drastic that the nucleus cannot recover.
incident neutron – the nucleus absorbed causes the nucleus to undergo deformation. In around 10-14 seconds, one of the deformations is so drastic that the nucleus cannot recover.
![]() splitting of nucleus – the nucleus fissions, releasing an average of two to three neutrons.
splitting of nucleus – the nucleus fissions, releasing an average of two to three neutrons.
![]() fission nucleus – in around 10-12 seconds, the fission fragments lose their kinetic energy and come to rest, emitting a number of gamma rays. Now the fragments are called fission products.
fission nucleus – in around 10-12 seconds, the fission fragments lose their kinetic energy and come to rest, emitting a number of gamma rays. Now the fragments are called fission products.
![]() incident neutrons – the fission products lose their excess energy by radioactive decay, emitting particles over a lengthy time period (seconds to years).
incident neutrons – the fission products lose their excess energy by radioactive decay, emitting particles over a lengthy time period (seconds to years).
![]() other more fission product – the course of a chain reaction is determined by the probability that a neutron released in fission will cause a subsequent fission.
other more fission product – the course of a chain reaction is determined by the probability that a neutron released in fission will cause a subsequent fission.
oooo
oooo
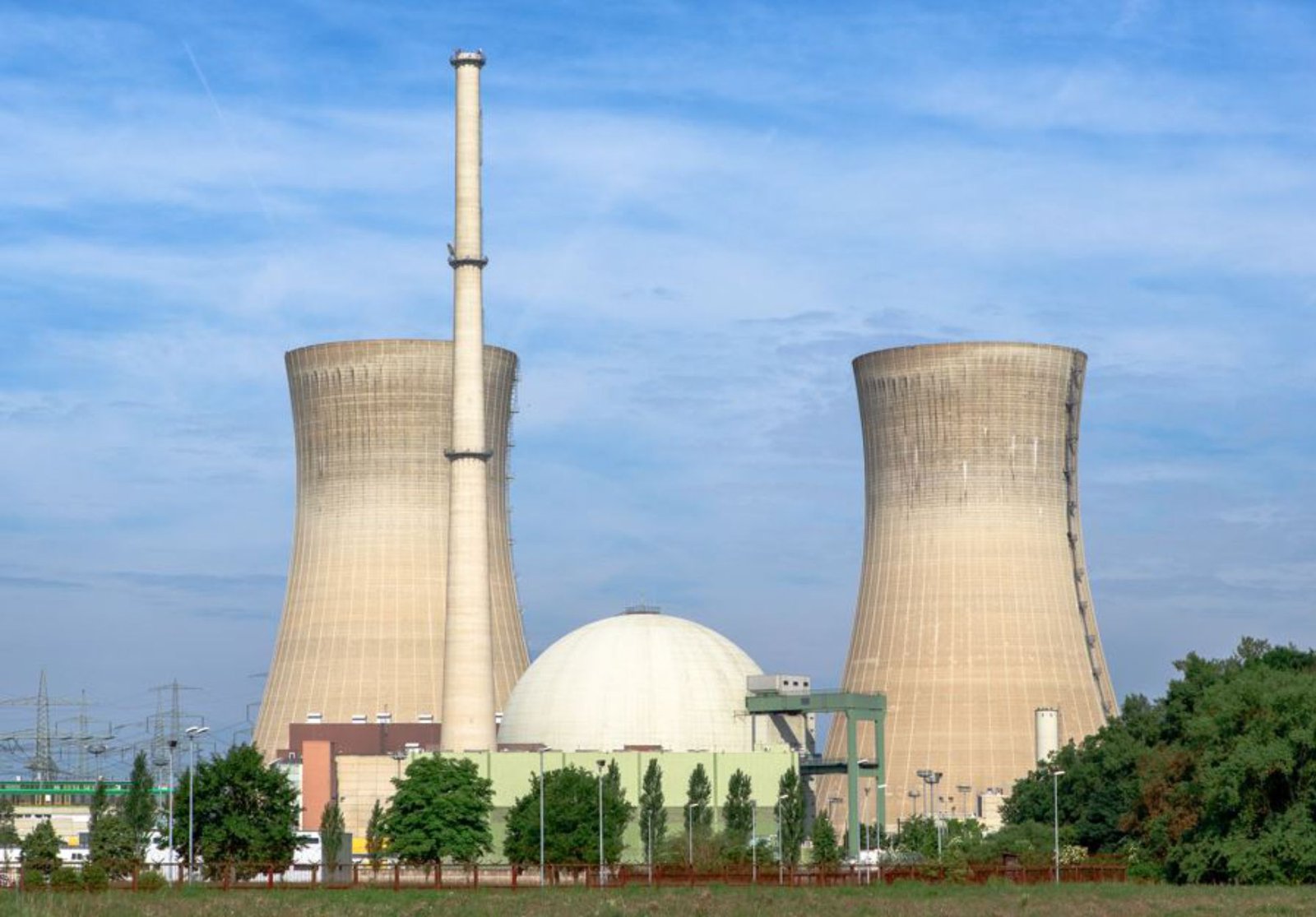
Nuclear Power Plant
oooo
oooo

oooo
- nuclear fission takes place inside the reactor of a nuclear power plant.
o - nuclear power plants heat water to produce steam.
o - nuclear power plants use heat produced during nuclear fission to heat water.
o

BSL Version
oooo
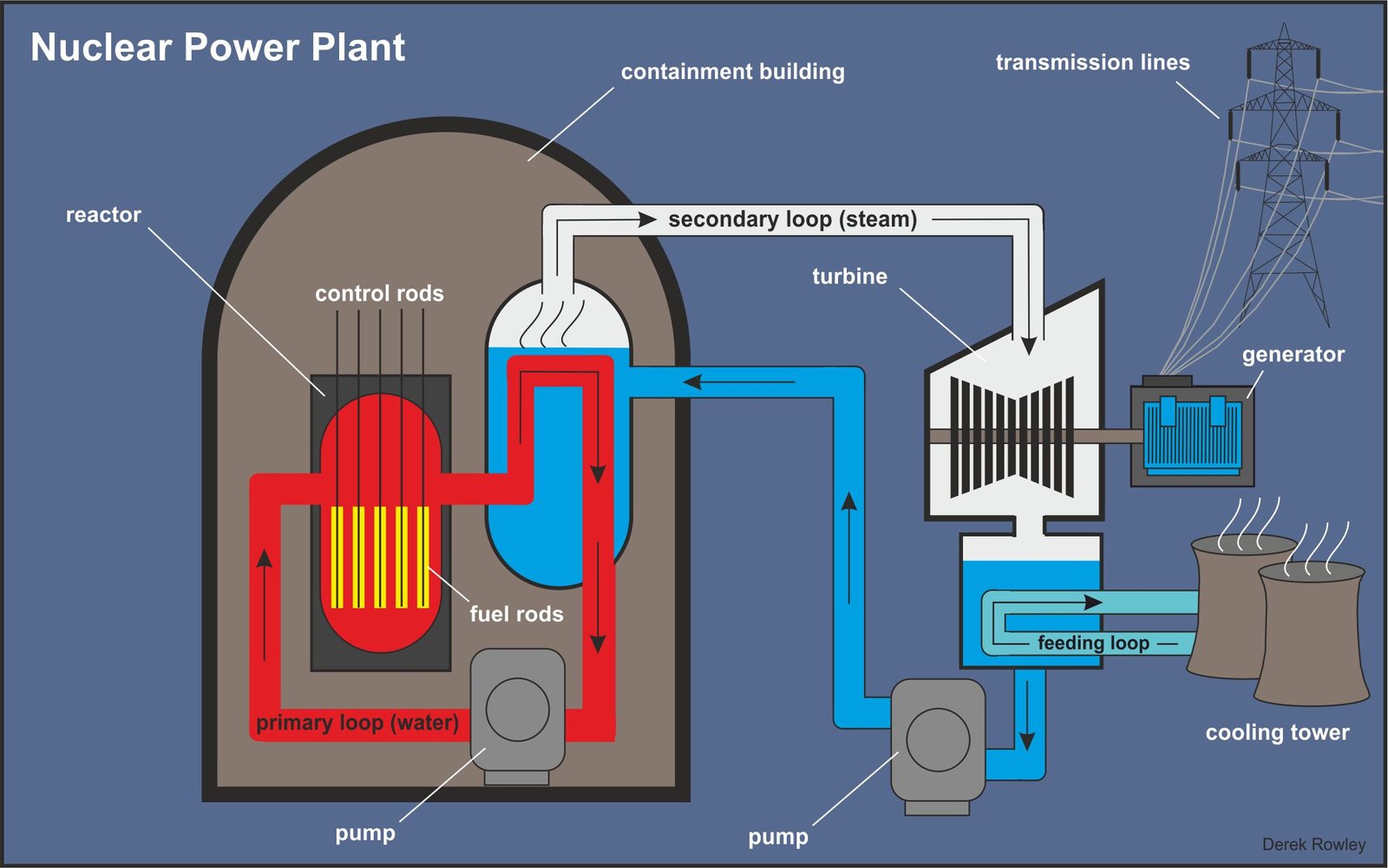
- in nuclear fission, atoms are split apart to form smaller atoms, releasing energy.
o
o
oooo
Atomic bomb
oooo
oooo
Fusion / Fission
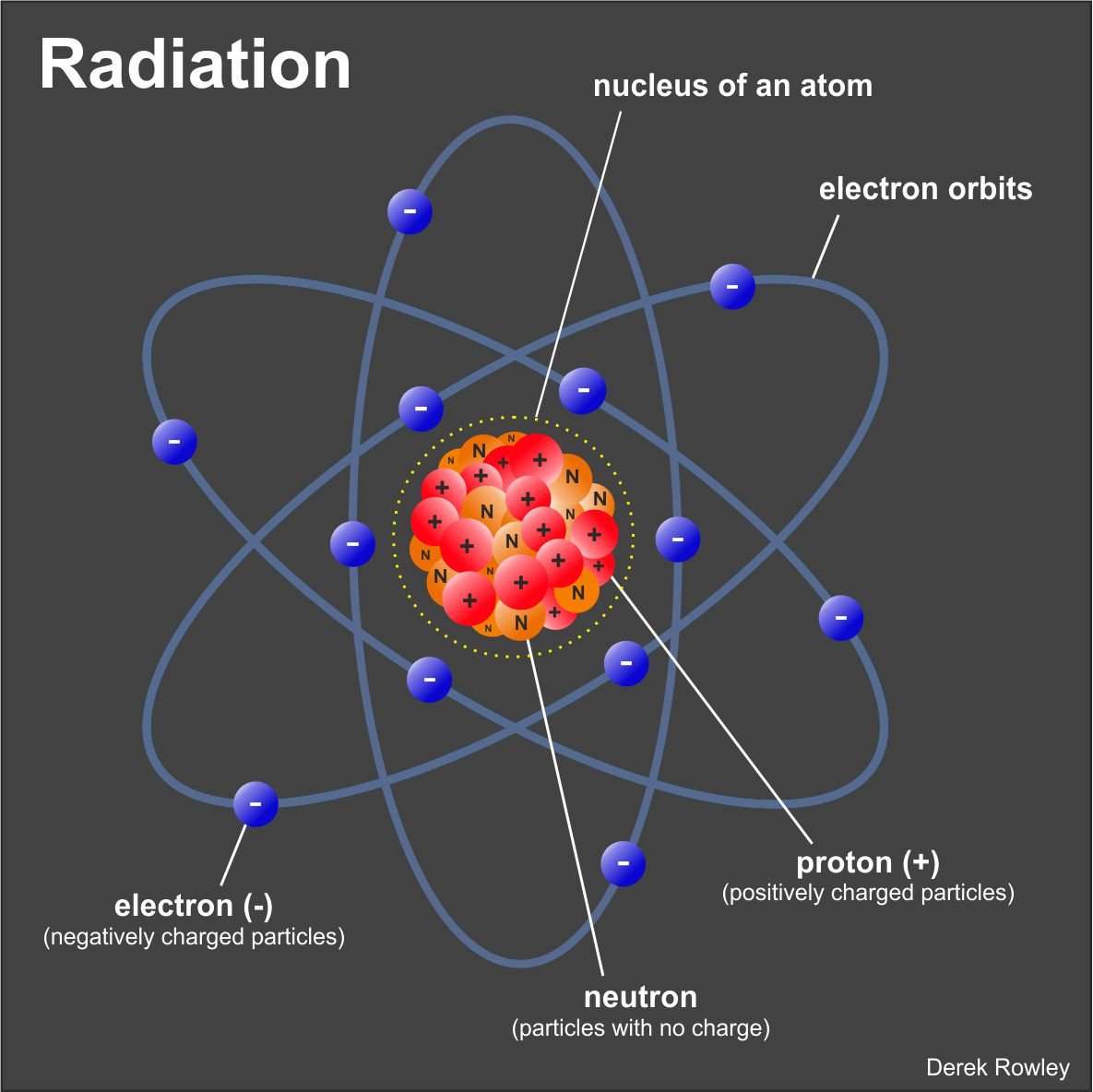
Atoms
The atom comprises three particles:
electrons (-), protons (+) and neutrons.
oooo
oooo
oooo
- every star in the universe – it can be released either by nuclear fusion or nuclear fission.
o - the energy that holds the nucleus of every atom together is called nuclear energy.
o - nuclear energy fuels nuclear power stations, and every star in the universe – it can be released either by fission or fusion.
o - energy that is given out by atoms at high speed is called radiation – two main forms; electromagnetic radiation and atomic particles.
o - nuclei – usually only tiny nuclei, such as those of hydrogen and helium, fuse (join); only under extreme pressure in huge, exploding stars do big nuclei – such as those of iron.
o - nuclear fission – it happens when nuclear energy is released by the splitting of nuclei; this method used in most power stations and in atomic bombs – involves splitting big nuclei; such as Uranium-235 and plutonium.
o - when a nucleus splits, it gives out gamma rays, neutrons (see atom) and intense heat.
o - in an atomic bomb – the energy is released in one second!
o - in a power station – control rods ensure that nuclear reactions are slowed down to release energy gradually.
o
o
oooo
oooo
oooo

BSL Version
oooo
oooo
oooo
Did you know?
o
How powerful between mankind and natural universe?
oooo

mankind: Hiroshima bomb at Japan – released 84 trillion joules of energy.
o

- natural universe: Supernova – releases 125,000 trillion trillion times as much. (Messier 1 – Crab Nebula; seen by a telescope.)
oooo
oooo
oooo
oooo
Back to The Universe / next to X-rays in space page.
oooo