oooo
oooo
oooo
oooo


BSL Version
o
- The Big Bang is the idea that the universe began as just a single point, then expanded and stretched to grow as large as it is right now and it is still stretching.
o
o
o
oooo
What is the current understanding of the Big Bang?
o
Events happened very very quickly at the beginning of the Universe!
oooo
oooo
oooo
oooo
oooo
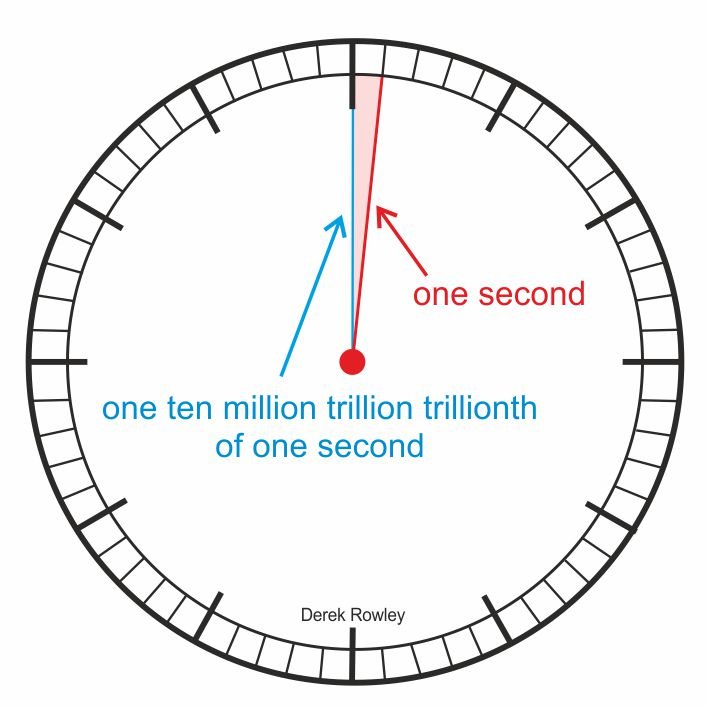
- One ten million trillion trillion trillionth of a second
In order to explain what happened scientists use measurements of time that are very small.
o
- At first…
The Universe was unspeakably small and hot – getting larger and cooler ever since.
o
o
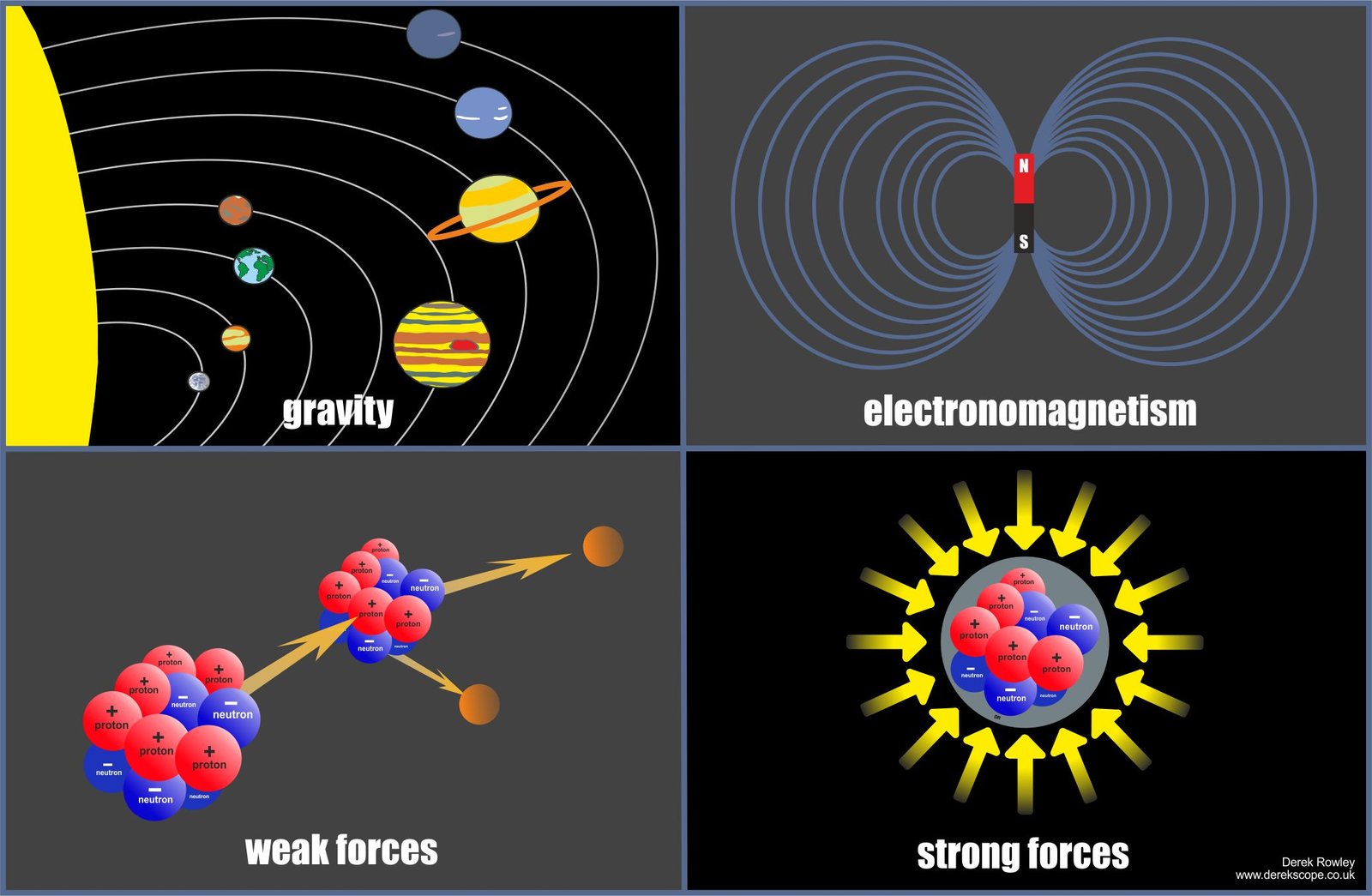
Four fundamental forces
oooo
- Four fundamental forces govern interactions between all objects in the universe.
o - This illustration shows above the four fundamental forces of the universe (clockwise from top left):
o
– gravity
– electromagnetism
– weak forces
– strong forces
o
oooo
oooo
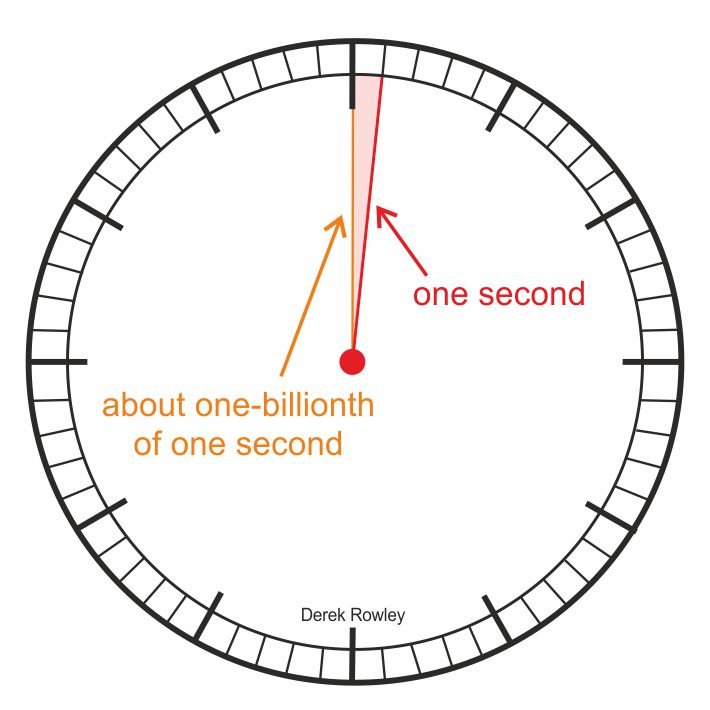
About one-billionth of one second…
oooo
oooo
oooo
oooo
- About one-billionth of one second after the Big Bang.
o - The Universe lay in a dense sea of quarks, where the first particles (neutrons and protons) were beginning to form.
o
o
Dense sea of quarks
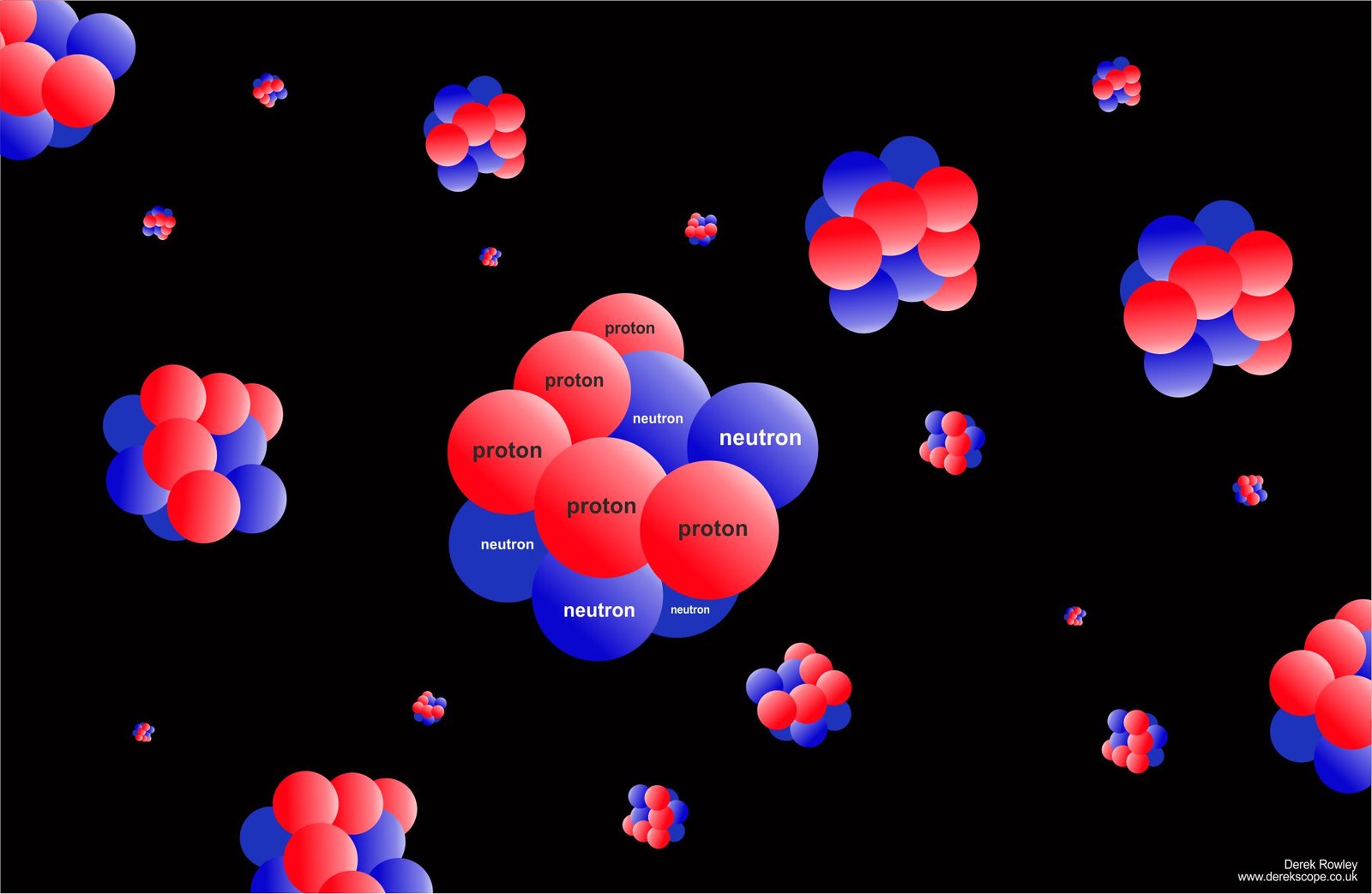
- A quark is a tiny particle which makes up protons (postive +) and neutrons (negative -).
o
o
oooo
oooo
oooo
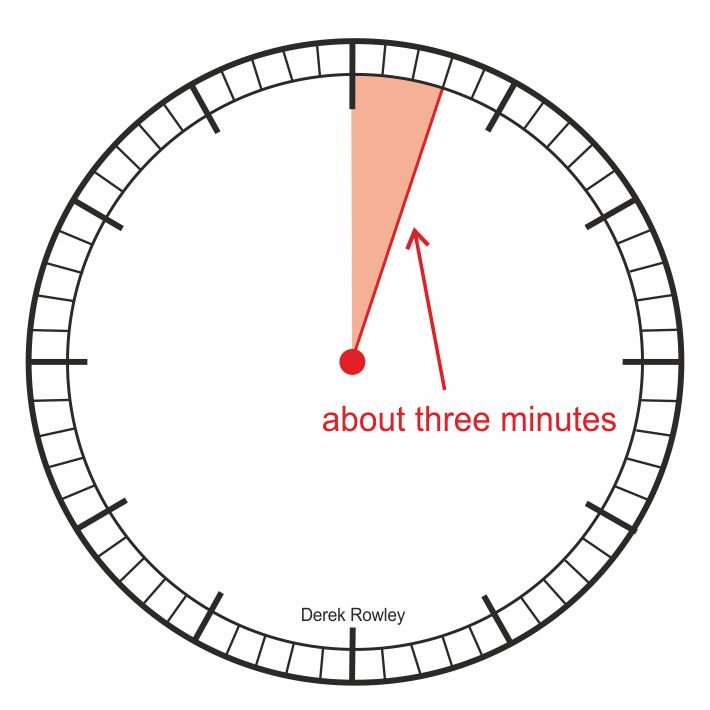
About three minutes…
oooo
oooo
oooo
- About three minutes after the Big Bang there was a brief period of nucleosynthesis when quarks joined together to form protons (+), and neutrons (-).
o - First nuclei – Hydrogen and helium formed.
o
o
oooo
For the first 380,000 years after the Big Bang
oooo
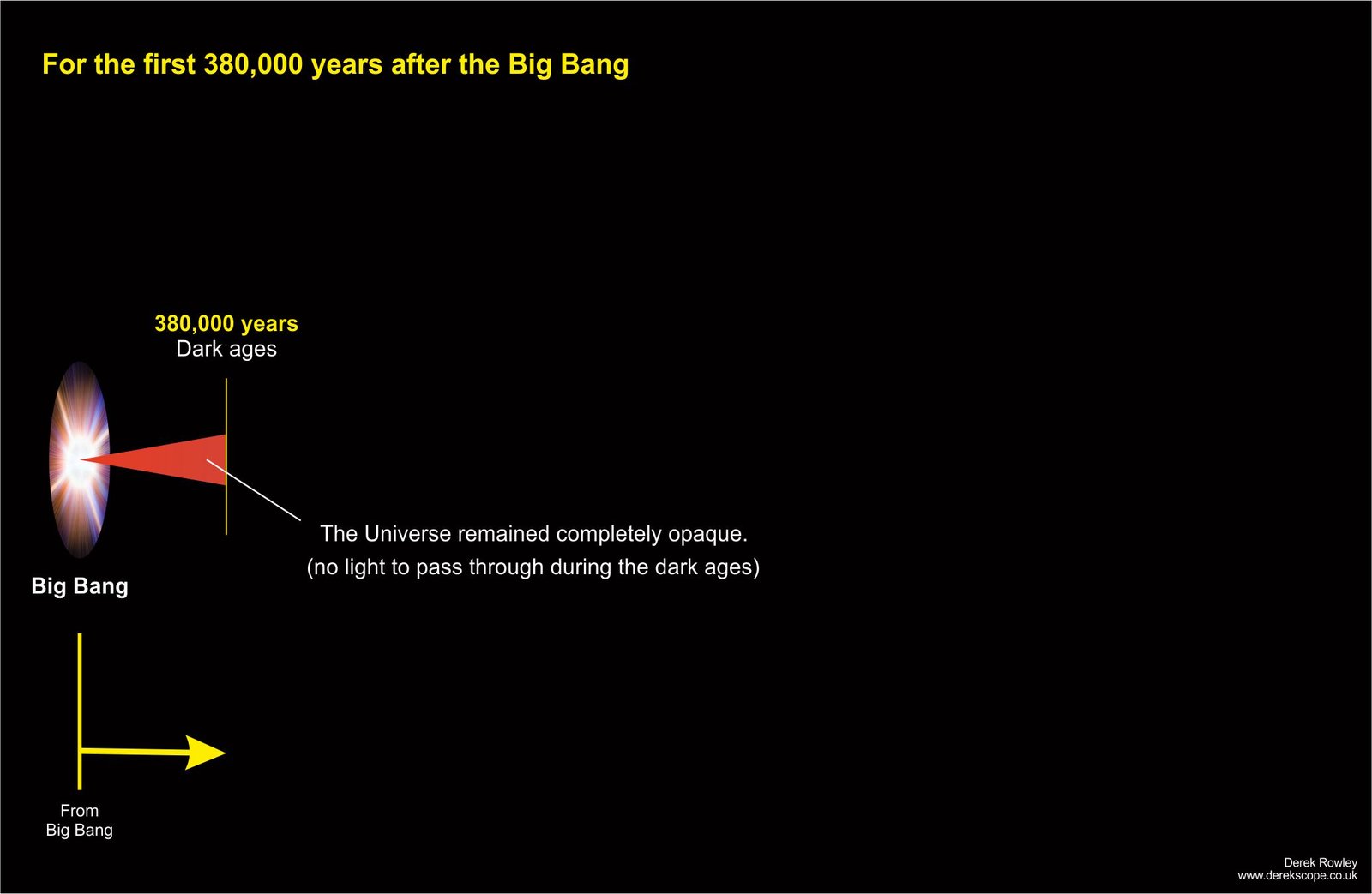
- The early Universe after the Bang Big completely opaque (like a thick fog ~ no light to pass through during the dark ages).
o - Because the super-hot plasma where the light (photons) constantly scattered off free electrons and protons, preventing it from travelling far.
o - During this period, the temperature was so high that electrons and protons could not combine to form neutral atoms.
o - This “cosmic fog” cleared as the universe expanded and cooled enough for electrons and protons to form neutral atoms (recombination), allowing light to travel freely.
o
After 380,000 years…
oooo
- The Universe cooled enough for electrons and nuclei to combine, forming neutral atoms (mostly hydrogen and helium), making the universe transparent and releasing the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) radiation.
o - Then it become cool enough for protons (+) and neutrons (-) to capture electrons.
o - The first atoms form.
o
o
oooo
200 million years after the Big Bang
oooo
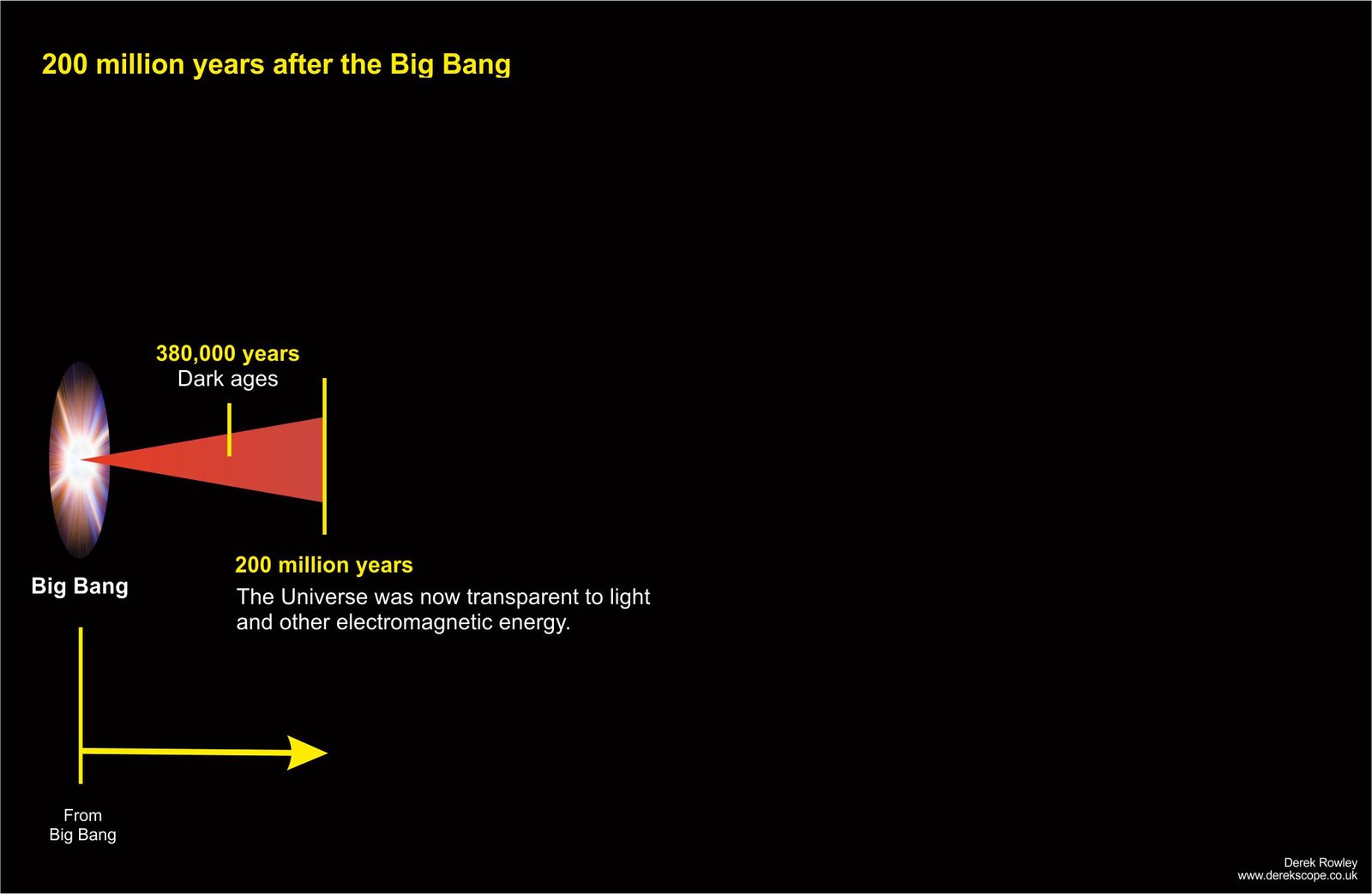
- After recombination, the universe was filled with neutral gas (mostly hydrogen and helium), but no stars or galaxies yet existed, so it was dark.
o - Gravity pulled gas and dark matter together, forming dense clouds that ignited into the first massive stars (Population III stars) and the first small galaxies, ending the Dark Ages.
o - The Universe remained completely opaque.
o - Then it become cool enough for protons (+) and neutrons (-) to capture electrons and form atoms.
oooo
oooo
oooo
About 300 million years after the Big Bang
oooo
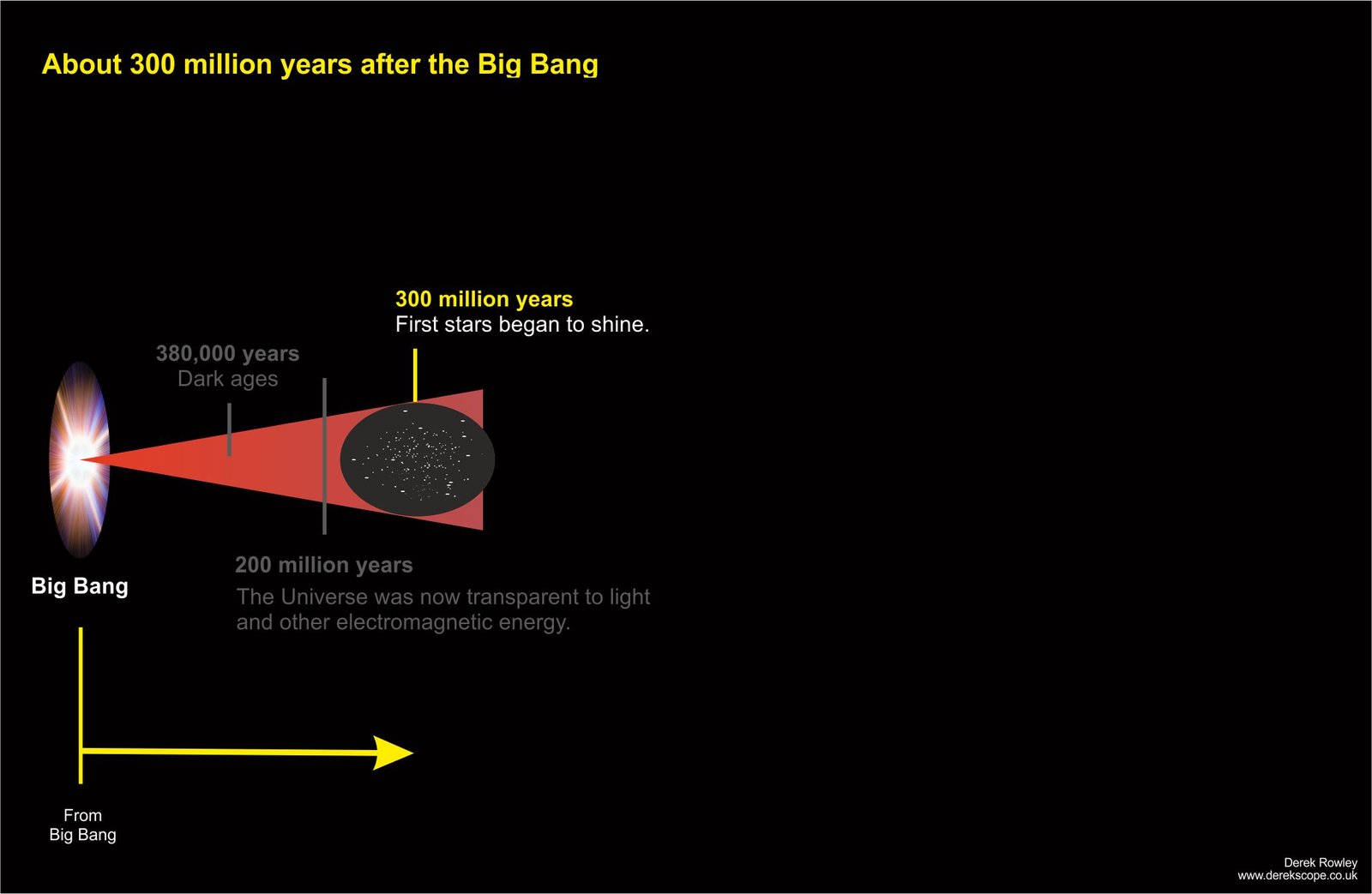
- The first stars began to shine.
oooo
oooo
oo
500 million years after the Big Bang
oooo
- Dark matter forms a scaffolding or filamentary strands across the universe, and galaxies appear along these strands.
o - Gas falls into the halo ~ ordinary matter (hydrogen, helium) is pulled into these halos as it cools and condenses, it forms: stars, star clusters and full galaxies.
o
o
(![]() Click here to see the meaning of the filamentary Comic Web.)
Click here to see the meaning of the filamentary Comic Web.)
oooo
1 billion years after the Big Bang
oooo
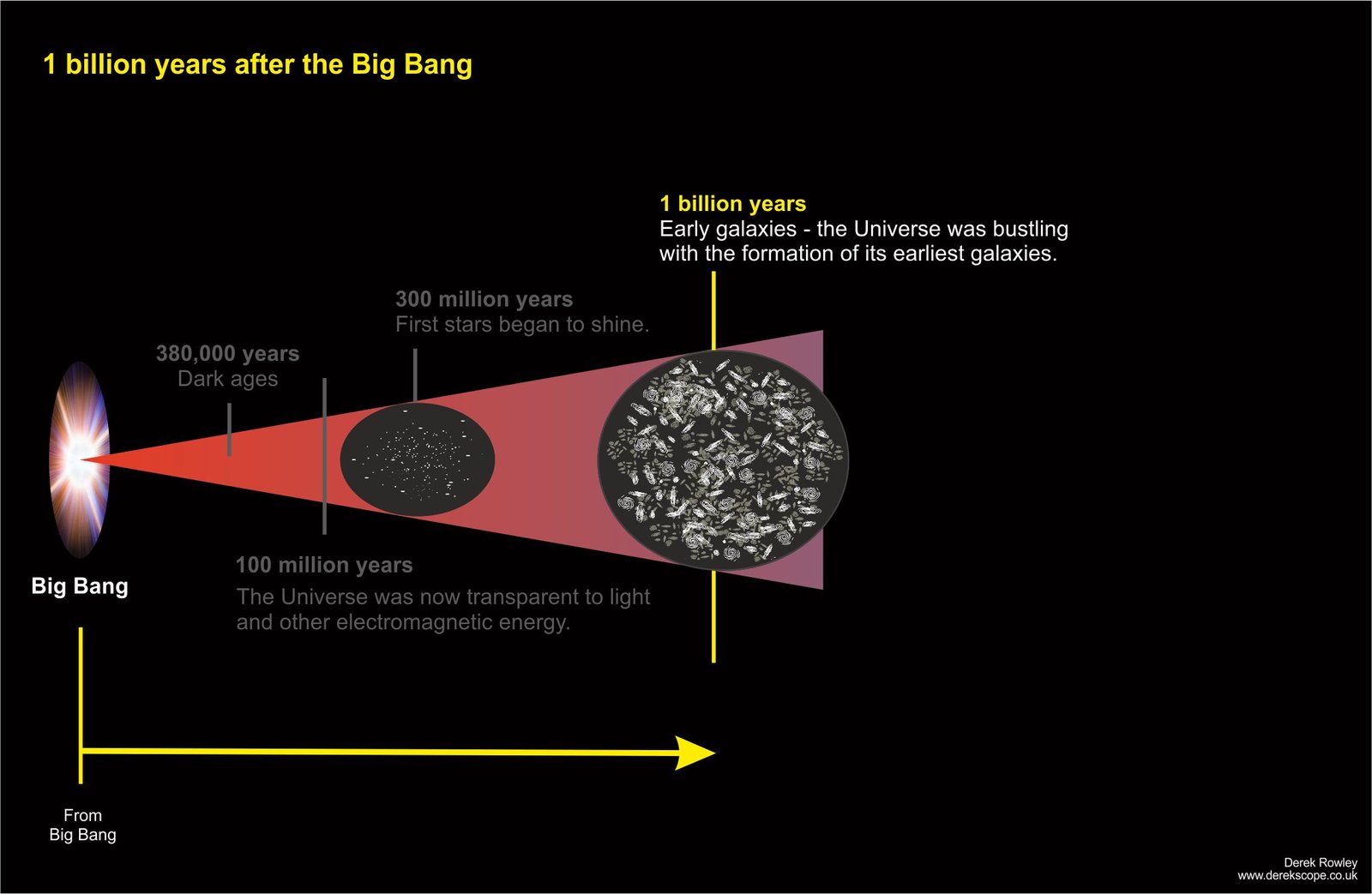
- Galaxies and Dark Matter ~ galaxies form in dark matter cradles on cosmic structure.
o - Dark matter collapes first ~ after the Big Bang, dark matter began clumping under gravity. Because it doesn’t interact with light or radiation, it could collapse earlier.
o - Without dark matter’s stabilising gravitational pull, galaxies would not have formed or held together in the shapes.
o - These clumps become “halos” ~ each halo is a gravitational bubble (a region where dark matter density is high.)
o
oooo
13.8 billion years after the Big Bang
oooo
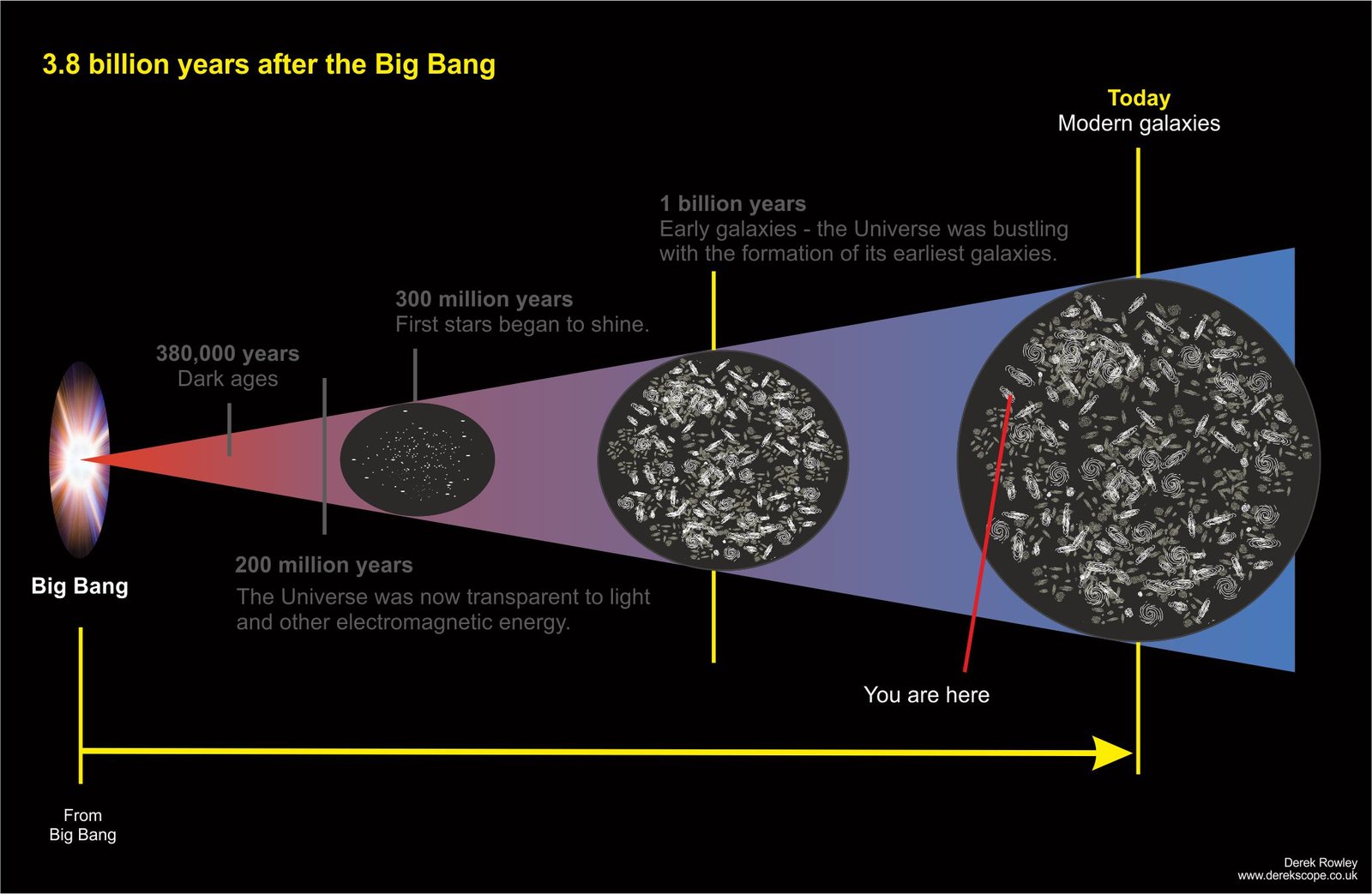
- Today Universe is epanding faster than ever ~ driven by dark energy.
o - Cooling slowly, now around -274°C.
o - Growing more structured, with galaxies clustering into filaments and voids.
o - There is still much to be discovered about the Universe and the Big Bang.
oooo
oooo
oooo
Back to The Universe / next to The Cosmic Microwave Background page.